Comparison of 1-Year Clinical Outcomes Between Ticagrelor Versus Clopidogrel in Type 2 Diabetes Patients After Implantation of Small Diameter Stents
- PMID: 39763313
- PMCID: PMC11793804
- DOI: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2024.4603
Comparison of 1-Year Clinical Outcomes Between Ticagrelor Versus Clopidogrel in Type 2 Diabetes Patients After Implantation of Small Diameter Stents
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with small-diameter stents (SDS), that are equal to or less than 2.5 mm in diameter, face increased risks of restenosis and complications. This study aimed to evaluate the 1-year follow-up to assess the rate of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) and bleeding risk between ticagrelor and clopidogrel in T2DM patients after SDS implantation.
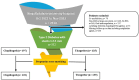
Methods: The study was a single-center, prospective controlled registry trial, which included 332 T2DM patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention with SDS implantation. Follow-up was conducted for 1 year.
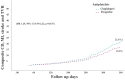
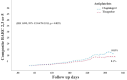
Results: Following propensity score matching, the 1-year analysis revealed no significant difference in the risk of the composite MACE between clopidogrel and ticagrelor groups (P = .295). Male gender, history of ischemic heart disease, ejection fraction (EF), coronary lesion type, and chronic kidney disease (CKD) were identified as potential predictors for the composite endpoint. In a subanalysis of CKD patients, the 12-month rates of composites of cardiac death (CD), myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and target vessel revascularization (TVR) were lower in the ticagrelor group than in the clopidogrel group (P = .024). However, the ticagrelor group was associated with a higher rate of bleeding compared to the clopidogrel group (20% vs. 9%) (P = .041).
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that ticagrelor did not show improvement in the composite of CD, MI, stroke, TVR, or the risk of bleeding events defined by the BARC criteria in patients with T2DM and SDS compared with clopidogrel emphasizing the importance of individualized treatment decisions based on patient characteristics. However, the results may not be representative of the entire population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy assessment of ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in Chinese patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention by data mining and machine-learning decision tree approaches.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020 Oct;45(5):1076-1086. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13172. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020. PMID: 32627223
-
Net clinical benefit of clopidogrel versus ticagrelor in elderly patients carrying CYP2C19 loss-of-function variants with acute coronary syndrome after percutaneous coronary intervention.Atherosclerosis. 2024 Mar;390:117395. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2023.117395. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Atherosclerosis. 2024. PMID: 38114408
-
Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in acute myocardial infarction patients with multivessel disease; From Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry-National Institute of Health.J Cardiol. 2020 May;75(5):478-484. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2019.11.003. Epub 2019 Dec 16. J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31859138
-
Ticagrelor or Clopidogrel as Antiplatelet Agents in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: A Meta-analysis.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2023 Sep;23(5):533-546. doi: 10.1007/s40256-023-00600-w. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37530990
-
Ticagrelor or Clopidogrel Monotherapy vs Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Systematic Review and Patient-Level Meta-Analysis.JAMA Cardiol. 2024 May 1;9(5):437-448. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2024.0133. JAMA Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38506796 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
What is the Optimal Antiplatelet Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Small Diameter Stents?Anatol J Cardiol. 2025 May 26;29(8):448-9. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2025.5347. Online ahead of print. Anatol J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40418167 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Letter to the Editor: "What Is the Optimal Antiplatelet Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Small Diameter Stents?".Anatol J Cardiol. 2025 Jun 30;29(8):450-1. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2025.5348. Online ahead of print. Anatol J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40589136 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zelniker TA, Wiviott SD, Raz I, et al. Comparison of the effects of glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for prevention of major adverse cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2019;139(17):2022 2031. (10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038868) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Handelsman Y, Bloomgarden ZT, Grunberger G, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology–Clinical practice guidelines for developing a diabetes mellitus comprehensive care plan–2015—executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2015;21(4):413 437. (10.4158/EP15672.GL) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources