Small-molecule MMRi36 induces apoptosis in p53-mutant lymphomas by targeting MDM2/MDM4/XIAP for degradation
- PMID: 39763603
- PMCID: PMC11700832
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1462231
Small-molecule MMRi36 induces apoptosis in p53-mutant lymphomas by targeting MDM2/MDM4/XIAP for degradation
Abstract
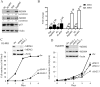
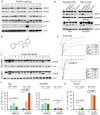
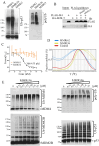
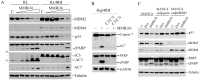
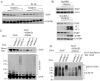
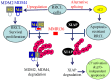
Rituximab combined with systemic chemotherapy significantly improves the rate of complete response in B-cell lymphomas. However, acquired rituximab resistance develops in most patients leading to relapse. The mechanisms underlying rituximab resistance are not well-understood. MDM2 and MDM4 proteins are major negative regulators of p53, but they also have p53-independent activities in mouse models of lymphomagenesis. Whether MDM2 or MDM4 is involved in rituximab resistance has not been explored. Here we report that MDM2 and MDM4 are upregulated in p53-mutant rituximab-resistant cells by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. Knockdown of MDM2 or MDM4 significantly hindered growth of rituximab-resistant cells. To explore whether targeting the RING-domain of MDM2-MDM4 heterodimers is a viable strategy for the treatment of rituximab-resistant lymphomas, we identified MMRi36 in a high throughput small-molecule screen. Here we show that MMRi36 binds and stabilizes MDM2-MDM4 RING heterodimers and acts as an activator of the MDM2-MDM4 E3 ligase complex in vitro and promotes proteasomal degradation of MDM2/MDM4 proteins in cells. MMRi36 potently induces p53-independent apoptosis in p53-mutant lymphoma cells and it exerts non-apoptotic anti-lymphoma effect in rituximab resistant cells. The pro-apoptotic mechanisms of MMRi36 involves activation of both caspase 3 and caspase 7 associated with increased polyubiquitination and degradation of XIAP. Therefore, MMRi36 is a novel prototype small-molecule for targeting MDM2/MDM4/XIAP for degradation and induction of apoptosis in p53-mutant lymphomas.
Keywords: MDM2; MDM4; MMRi36; Rituximab; XIAP; apoptosis; lymphoma; mutant p53.
Copyright © 2024 Lama, Wu, Mavis, Ruiz, Querol-García, Martin, Chemler, Chandra, Goodrich, Hernandez-Ilizaliturri, Muñoz and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Czuczman MS, Olejniczak S, Gowda A, Kotowski A, Binder A, Kaur H, et al. Acquirement of rituximab resistance in lymphoma cell lines is associated with both global CD20 gene and protein down-regulation regulated at the pretranscriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Clin Cancer Res. (2008) 14:1561–70. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1254 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

