This is a preprint.
A new class of penicillin-binding protein inhibitors to address drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- PMID: 39763734
- PMCID: PMC11703265
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.27.630553
A new class of penicillin-binding protein inhibitors to address drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Abstract
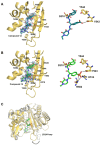
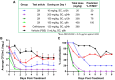
β-Lactams are the most widely used antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial infections because of their proven track record of safety and efficacy. However, susceptibility to β-lactam antibiotics is continually eroded by resistance mechanisms. Emerging multidrug-resistant (MDR) Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains possessing altered penA alleles (encoding PBP2) pose a global health emergency as they threaten the utility of ceftriaxone, the last remaining outpatient antibiotic. Here we disclose a novel benzoxaborinine-based penicillin-binding protein inhibitor series (boro-PBPi) that is envisioned to address penA-mediated resistance while offering protection against evolution and expansion of β-lactamases. Optimization of boro-PBPi led to the identification of compound 21 (VNRX-14079) that exhibits potent antibacterial activity against MDR N. gonorrhoeae achieved by high affinity binding to the PBP2 target. Boro-PBPi/PBP2 complex structures confirmed covalent interaction of the boron atom with Ser310 and the importance of the β3-β4 loop for improved affinity. 21 elicits bactericidal activity, a low frequency of resistance, a good safety profile, suitable pharmacokinetic properties, and in vivo efficacy in a murine infection model against ceftriaxone-resistant N. gonorrhoeae. 21 is a promising anti-gonorrhea agent poised for further advancement.
Keywords: PBP inhibitor; antibiotic; boron; gonorrhea; non-β-lactam; penicillin-binding protein.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests Authors T.U., A.L.Z., B.M., L.M.A., S.A.B., C.L.C., G.H.C., A.S.D., M.E., S.G.E.H., C.L.M., G.R., A.S., K.U., F.Y., D.C.P, C.J.B., D.M.D., and S.M.C. are current or former employees of Venatorx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. T.U., A.L.Z., S.A.B., C.L.C., G.H.C., C.L.M., D.C.P., C.J.B., D.M.D., and S.M.C. are co-inventors on a patent application covering molecules described in this manuscript.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
