This is a preprint.
Transcriptional responses to in vitro macrocyclic lactone exposure in Toxocara canis larvae using RNA-seq
- PMID: 39763735
- PMCID: PMC11702694
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.20.629602
Transcriptional responses to in vitro macrocyclic lactone exposure in Toxocara canis larvae using RNA-seq
Update in
-
Transcriptional responses to in vitro macrocyclic lactone exposure in Toxocara canis larvae using RNA-seq.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2025 Dec;29:100614. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2025.100614. Epub 2025 Sep 19. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40983028 Free PMC article.
Abstract
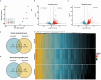
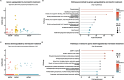
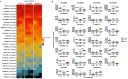
Toxocara canis, the causative agent of zoonotic toxocariasis in humans, is a parasitic roundworm of canids with a complex lifecycle. While macrocyclic lactones (MLs) are successful at treating adult T. canis infections when used at FDA-approved doses in dogs, they fail to kill somatic third-stage larvae. In this study, we profiled the transcriptome of third-stage larvae derived from larvated eggs and treated in vitro with 10 μM of the MLs - ivermectin and moxidectin with Illumina sequencing. We analyzed transcriptional changes in comparison with untreated control larvae. In ivermectin-treated larvae, we identified 608 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), of which 453 were upregulated and 155 were downregulated. In moxidectin-treated larvae, we identified 1,413 DEGs, of which 902 were upregulated and 511 were downregulated. Notably, many DEGs were involved in critical biological processes and pathways including transcriptional regulation, energy metabolism, neuronal structure and function, physiological processes such as reproduction, excretory/secretory molecule production, host-parasite response mechanisms, and parasite elimination. We also assessed the expression of known ML targets and transporters, including glutamate-gated chloride channels (GluCls), and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, subfamily B, with a particular focus on P-glycoproteins (P-gps). We present gene names for previously uncharacterized T. canis GluCl genes using phylogenetic analysis of nematode orthologs to provide uniform gene nomenclature. Our study revealed that the expression of Tca-glc-3 and six ABCB genes, particularly four P-gps, were significantly altered in response to ML treatment. Compared to controls, Tca-glc-3, Tca-Pgp-11.2, and Tca-Pgp-13.2 were downregulated in ivermectin-treated larvae, while Tca-abcb1, Tca-abcb7, Tca-Pgp-11.2, and Tca-Pgp-13.2 were downregulated in moxidectin-treated larvae. Conversely, Tca-abcb9.1 and Tca-Pgp-11.3 were upregulated in moxidectin-treated larvae. These findings suggest that MLs broadly impact transcriptional regulation in T. canis larvae.
Keywords: ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters; Dogs; RNA-Seq; Toxocara canis; Toxocariasis; glutamate-gated chloride channels; ivermectin; mRNA; moxidectin; transcriptome.
Figures




References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
