This is a preprint.
Asymmetric Activation of Retinal ON and OFF Pathways by AOSLO Raster-Scanned Visual Stimuli
- PMID: 39763934
- PMCID: PMC11702774
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.17.628952
Asymmetric Activation of Retinal ON and OFF Pathways by AOSLO Raster-Scanned Visual Stimuli
Update in
-
Asymmetric activation of retinal ON and OFF pathways by AOSLO raster-scanned visual stimuli.Biomed Opt Express. 2025 Jun 9;16(7):2663-2691. doi: 10.1364/BOE.566008. eCollection 2025 Jul 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2025. PMID: 40677827 Free PMC article.
Abstract
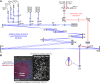
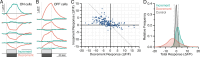
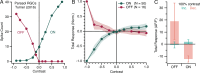
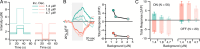
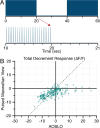
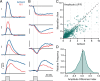
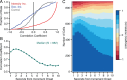
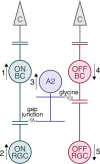
Adaptive optics scanning light ophthalmoscopy (AOSLO) enables high-resolution retinal imaging, eye tracking, and stimulus delivery in the living eye. AOSLO-mediated visual stimuli are created by temporally modulating the excitation light as it scans across the retina. As a result, each location within the field of view receives a brief flash of light during each scanner cycle (every 33-40 ms). Here we used in vivo calcium imaging with AOSLO to investigate the impact of this intermittent stimulation on the retinal ON and OFF pathways. Raster-scanned backgrounds exaggerated existing ON-OFF pathway asymmetries leading to high baseline activity in ON cells and increased response rectification in OFF cells.
Figures


References
-
- Bach M., Meigen T., and Strasburger H. (1997). Raster-scan cathode-ray tubes for vision research - limits of resolution in space, time and intensity. Spatial Vision, 10(4):403–414. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
