This is a preprint.
HapCNV: A Comprehensive Framework for CNV Detection in Low-input DNA Sequencing Data
- PMID: 39763944
- PMCID: PMC11702719
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.19.629494
HapCNV: A Comprehensive Framework for CNV Detection in Low-input DNA Sequencing Data
Abstract
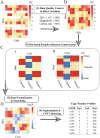
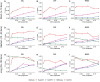
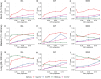
Copy number variants (CNVs) are prevalent in both diploid and haploid genomes, with the latter containing a single copy of each gene. Studying CNVs in genomes from single or few cells is significantly advancing our knowledge in human disorders and disease susceptibility. Low-input including low-cell and single-cell sequencing data for haploid and diploid organisms generally displays shallow and highly non-uniform read counts resulting from the whole genome amplification steps that introduce amplification biases. In addition, haploid organisms typically possess relatively short genomes and require a higher degree of DNA amplification compared to diploid organisms. However, most CNV detection methods are specifically developed for diploid genomes without specific consideration of effects on haploid genomes. Challenges also reside in reference samples or normal controls which are used to provide baseline signals for defining copy number losses or gains. In traditional methods, references are usually pre-specified from cells that are assumed to be normal or disease-free. However, the use of pre-defined reference cells can bias results if common CNVs are present. Here, we present the development of a comprehensive statistical framework for data normalization and CNV detection in haploid single- or low-cell DNA sequencing data called HapCNV. The prominent advancement is the construction of a novel genomic location specific pseudo-reference that selects unbiased references using a preliminary cell clustering method. This approach effectively preserves common CNVs. Using simulations, we demonstrated that HapCNV outperformed existing methods by generating more accurate CNV detection, especially for short CNVs. Superior performance of HapCNV was also validated in detecting known CNVs in a real P. falciparum parasite dataset. In conclusion, HapCNV provides a novel and useful approach for CNV detection in haploid low-input sequencing datasets, with easy applicability to diploids.
Keywords: Copy number variation; Haploid; Low-input sequencing; Pseudo-reference sequence; Single-cell DNA sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guryev V., et al. , Distribution and functional impact of DNA copy number variation in the rat. Nat Genet, 2008. 40(5): p. 538–45. - PubMed
-
- Pereira K.M.C., et al. , Impact of C4, C4A and C4B gene copy number variation in the susceptibility, phenotype and progression of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Rheumatol, 2019. 59(1): p. 36. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
