Exploring the role of noncoding RNAs in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and precision medicine
- PMID: 39764154
- PMCID: PMC11703603
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.06.015
Exploring the role of noncoding RNAs in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and precision medicine
Abstract
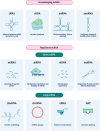
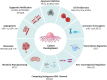
This review article studies the complex field of noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) in cancer biology, focusing on their potential use as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. NcRNAs include circular RNAs (circRNAs), long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), and microRNAs (miRNAs). We discuss how ncRNAs affect gene expression in cancerous cells, the spread of cancer, and metastasis. The article illustrates the complex pathways through which ncRNAs can affect oncogenesis, tumor suppression, and therapeutic resistance. It also assesses the potential clinical uses of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), including their utility in cancer diagnosis, and prognosis. Besides, their potential for personalized cancer therapy is documented. Finally, it is concluded that understanding the role of ncRNA is of clinical importance regarding carcinogenesis, cancer diagnosis, and personalized therapy.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cancer biology; Circular RNAs (circRNAs); Diagnosis; Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs); MicroRNAs (miRNAs); Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs); Personalized medicine; Prognosis.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive review and in silico analysis of the role of noncoding RNAs in retinoblastoma: A step-toward ncRNA precision.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jun;311(Pt 4):144036. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.144036. Epub 2025 May 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40345278 Review.
-
Which long noncoding RNAs and circular RNAs contribute to inflammatory bowel disease?Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jun 15;11(6):456. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2657-z. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32541691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Unlocking the Power of Non-Coding RNAs in Revolutionizing Cancer Therapy.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2025 Feb 26. doi: 10.2174/0115701638333005250128075758. Online ahead of print. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2025. PMID: 40012378
-
The significance of exosomal non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in the metastasis of colorectal cancer and development of therapy resistance.Gene. 2025 Feb 10;937:149141. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.149141. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Gene. 2025. PMID: 39643147 Review.
-
Crosstalk between non-coding RNAs and programmed cell death in colorectal cancer: implications for targeted therapy.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2025 Jan 15;18(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13072-024-00560-8. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2025. PMID: 39810224 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of CircHIPK3 biomarker potential in breast cancer.Pract Lab Med. 2025 Mar 20;45:e00470. doi: 10.1016/j.plabm.2025.e00470. eCollection 2025 Jul. Pract Lab Med. 2025. PMID: 40226123 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the mysteries of MEG3 LncRNA and its implications in genitourinary cancers.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 2;15:1519103. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1519103. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40242248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of circular RNAs in colorectal cancer: insights into biomarker discovery and therapeutic targeting.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 4;15:1549046. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1549046. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40687415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis rewired: ncRNA gatekeepers as pharmacological targets in hepatocellular carcinoma.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 7. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04404-4. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40622592 Review.
References
-
- Saleh R.O., et al. lncRNA-microRNA axis in cancer drug resistance: particular focus on signaling pathways. Med. Oncol. 2024;41(2):52. - PubMed
-
- Najafi S., et al. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs); roles in tumorigenesis and potentials as biomarkers in cancer diagnosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2022;418(2) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

