Comparison of Band Percentage vs Immature Granulocyte Percentage in the Setting of Possible Infection Principle Investigators
- PMID: 39764354
- PMCID: PMC11703591
- DOI: 10.1155/ah/3616532
Comparison of Band Percentage vs Immature Granulocyte Percentage in the Setting of Possible Infection Principle Investigators
Abstract
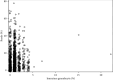
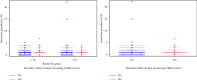
Background: Sepsis is a major cause of mortality worldwide. Early identification and treatment are critical to improve survival. Band count has been used as part of SIRS criteria for the early identification of potentially septic patients. Unfortunately, band count requires manual interpretation. This leads to increased potential for intraobserver variability. Immature granulocytes are counted in an automated fashion, which has the potential to improve accuracy and reduce costs. Research Objective: We aim to compare the band percentage and immature granulocyte percentage to set the threshold for immature granulocyte percentage equal to the sensitivity of > 10% band count. Methods: A retrospective chart review was conducted at a single academic medical center. Data from patients with SIRS criteria and measured immature granulocyte and band percentages were utilized to explore potential associations between immature granulocyte percentages and band percentages. Data were analyzed using Spearman correlations, Wilcoxon rank-sum tests, and logistic regressions. Results: We found no significant associations between immature granulocyte percentage and band percentage or other SIRS criteria. Conclusion: We conclude that immature granulocyte percentage does not correlate with band percentage in the setting of possible infection.
Copyright © 2024 Daniel Hershberger et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Performance evaluation of the immature granulocyte parameter on the Sysmex XE-2100 automated hematology analyzer.Lab Hematol. 2006;12(1):11-4. doi: 10.1532/LH96.05042. Lab Hematol. 2006. PMID: 16513542
-
[Predictive value of immature granulocytes for persistent systemic inflammatory response syndrome in patients with acute pancreatitis: analysis of 1 973 cases].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Dec;30(12):1123-1127. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.012.004. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 30592943 Chinese.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic significance of monitoring blood levels of immature neutrophils in patients with systemic inflammation.Crit Care. 2015 Feb 25;19(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0778-z. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 25887201 Free PMC article.
-
The use of granulocyte transfusion in neonatal sepsis.Transfus Med Rev. 1990 Jan;4(1):14-22. doi: 10.1016/s0887-7963(90)70244-1. Transfus Med Rev. 1990. PMID: 2134612 Review.
-
Immature Platelets As a Predictor of Disease Severity and Mortality in Sepsis and Septic Shock: A Systematic Review.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2020 Apr;46(3):320-327. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3400256. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2020. PMID: 31858518
References
-
- Zhu L., Chen G., Xia Q., et al. Use of Band Cell Percentage as an Early Predictor of Death and ICU Admission in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Hepato-Gastroenterology . 2010;57(104):1543–1548. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

