This is a preprint.
Agreement of Image Quality Metrics with Radiological Evaluation in the Presence of Motion Artifacts
- PMID: 39764402
- PMCID: PMC11703327
Agreement of Image Quality Metrics with Radiological Evaluation in the Presence of Motion Artifacts
Update in
-
Agreement of image quality metrics with radiological evaluation in the presence of motion artifacts.MAGMA. 2025 Dec;38(6):991-1002. doi: 10.1007/s10334-025-01266-y. Epub 2025 Jun 10. MAGMA. 2025. PMID: 40493331 Free PMC article.
Abstract
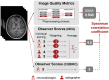
Object: Reliable image quality assessment is crucial for evaluating new motion correction methods for magnetic resonance imaging. We compare the performance of common reference-based and reference-free image quality metrics on unique datasets with real motion artifacts, and analyze the metrics' robustness to typical pre-processing techniques.
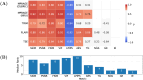
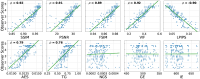
Materials and methods: We compared five reference-based and five reference-free metrics on brain data acquired with and without intentional motion (2D and 3D sequences). The metrics were recalculated seven times with varying pre-processing steps. Spearman correlation coefficients were computed to assess the relationship between image quality metrics and radiological evaluation.
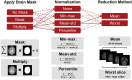
Results: All reference-based metrics showed strong correlation with observer assessments. Among reference-free metrics, Average Edge Strength offers the most promising results, as it consistently displayed stronger correlations across all sequences compared to the other reference-free metrics. The strongest correlation was achieved with percentile normalization and restricting the metric values to the skull-stripped brain region. In contrast, correlations were weaker when not applying any brain mask and using min-max or no normalization.
Discussion: Reference-based metrics reliably correlate with radiological evaluation across different sequences and datasets. Pre-processing significantly influences correlation values. Future research should focus on refining pre-processing techniques and exploring approaches for automated image quality evaluation.
Keywords: Artifacts; Data Quality; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Metrics; Motion.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Figures



References
-
- Tisdall M.D., Küstner T.: Metrics for motion and mr quality assessment. In: Advances in Magnetic Resonance Technology and Applications vol. 6, pp. 99–116. Elsevier, ??? (2022)
-
- Spieker V., Eichhorn H., Hammernik K., Rueckert D., Preibisch C., Karampinos D.C., Schnabel J.A.: Deep learning for retrospective motion correction in mri: A comprehensive review. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 43(2), 846–859 (2024) - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
