Isolation and characterization of cellulose-mineralizing haloalkaliphilic bacteria from Siberian soda lakes
- PMID: 39764452
- PMCID: PMC11700989
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1523074
Isolation and characterization of cellulose-mineralizing haloalkaliphilic bacteria from Siberian soda lakes
Abstract
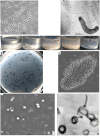
Soda lakes are unique double-extreme habitats characterized by high salinity and soluble carbonate alkalinity, yet harboring rich prokaryotic life. Despite intensive microbiology studies, little is known about the identity of the soda lake hydrolytic bacteria responsible for the primary degradation of the biomass organic matter, in particular cellulose. In this study, aerobic and anaerobic enrichment cultures with three forms of native insoluble cellulose inoculated with sediments from five soda lakes in south-western Siberia resulted in the isolation of four cellulotrophic haloalkaliphilic bacteria and their four saccharolytic satellites. The final aerobic enrichment included a cellulotrophic bacteroidetes (strain ABcell3) related to Sporocytophaga accompanied by a hemicellulolytic Marinimicrobium strain ABcell2. The anaerobic enrichments resolved in three primary cellulotrophic bacteria and their three saccharolytic bacteroidetes satellites. The culture selected on amorphous cellulose (ac) included a new cellulotrophic member of the Chitinispirillaceae (Fibrobacterota)-strain ANBcel5, and two different saccharolytic satellites from the Marinilabiliales and Balneolales orders. The final enrichment selected on Sigma 101 cellulose consisted of an endospore-forming cellulotrophic strain ANBcel31 belonging to the genus Herbivorax (Acetivibrionales) and its saccharolytic satellite from the Balneolales order. The anaerobic enrichment on a filter paper yielded a binary consortium with the cellulotrophic endospore-forming Halanaerobiales strain ANBcel28 in obligate syntrophy with a cellobiose-utilizing Natronincola. A functional genome analysis of the cellulotrophic isolates confirmed the presence of a large repertoire of genes encoding excreted cellulases, mostly from the GH9 and GH5 families, and indicated that in the endospore-forming anaerobic strains, ANBcel28 and ANBcel31 most of their endo-glucanases are assembled in cellulosomes. Overall, this study showed that cellulose can be mineralized in soda lakes at moderately saline and highly alkaline conditions either by aerobic or fermentative haloalkaliphilic bacteria.
Keywords: cellulase; cellulose; cellulotrophic bacteria; haloalkaliphilic; soda lakes.
Copyright © 2024 Sorokin, Merkel and Khizhniak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aikawa S., Baramee S., Sermsathanaswadi J., Thianheng P., Tachaapaikoon C., Shikata A., et al. (2018). Characterization and high-quality draft genome sequence of Herbivorax saccincola A7, an anaerobic, alkaliphilic, thermophilic, cellulolytic, and xylanolytic bacterium. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 41, 261–269. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2018.01.010, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

