The role of artificial intelligence in preoperative planning for Total Hip Arthroplasty: a systematic review
- PMID: 39764457
- PMCID: PMC11701226
- DOI: 10.3389/frai.2024.1417729
The role of artificial intelligence in preoperative planning for Total Hip Arthroplasty: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) is a transformative surgical intervention for hip joint disorders, necessitating meticulous preoperative planning for optimal outcomes. With the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI), preoperative planning paradigms have evolved, leveraging AI algorithms for enhanced decision support and imaging analysis. This systematic review aims to comprehensively evaluate the role of AI in THA preoperative planning, synthesizing evidence from studies exploring various AI techniques and their applications.
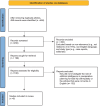
Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases was conducted to identify relevant articles. Inclusion criteria encompassed studies focusing on AI in THA preoperative planning, including randomized controlled trials (RCTs), observational studies, and comparative studies.
Results: Six studies from China met the inclusion criteria, collectively analyzing 831 patients. AI-assisted planning demonstrated superior accuracy in estimating prosthesis size and positioning compared to traditional methods. However, limitations such as geographic bias and language constraints were noted.
Conclusion: AI-assisted preoperative planning significantly enhances femoral positioning accuracy, providing superior outcomes compared to traditional methods. This improvement in precision, particularly in the placement of femoral and acetabular components, has been consistently observed across studies, making AI an indispensable tool in improving the overall success of Total Hip Arthroplasty. Despite promising findings, further research is warranted to address limitations and optimize the integration of AI technologies into routine clinical practice.
Keywords: Total Hip Arthroplasty; artificial intelligence; orthopedic; preoperative planning; systematic review.
Copyright © 2024 Mozafari, Moshtaghioon, Mahdavi, Ghaznavi, Behjat and Yeganeh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Value of 3D preoperative planning for primary total hip arthroplasty based on artificial intelligence technology.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Feb 24;16(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02294-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 33627149 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Emerging Technologies in Advancing Total Hip Arthroplasty.J Pers Med. 2025 Jan 9;15(1):21. doi: 10.3390/jpm15010021. J Pers Med. 2025. PMID: 39852213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Application of artificial intelligence preoperative planning system in total hip arthroplasty for adult developmental dysplasia of the hip].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Jan 15;37(1):25-30. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202209098. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36708111 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
The advantages of artificial intelligence-assisted total hip arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial followed by 12 months.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 22;10(22):e39664. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39664. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39624323 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence for image analysis in total hip and total knee arthroplasty : a scoping review.Bone Joint J. 2022 Aug;104-B(8):929-937. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.104B8.BJJ-2022-0120.R2. Bone Joint J. 2022. PMID: 35909383
Cited by
-
Applications of machine learning and deep learning in musculoskeletal medicine: a narrative review.Eur J Med Res. 2025 May 15;30(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02511-9. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40375335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Surgery: Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jun 25;6(7):e70260. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70260. eCollection 2025 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40567249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Musculoskeletal Care Using AI and Digital Health Applications: A Review of Commercial Solutions.HSS J. 2025 May 30:15563316251341321. doi: 10.1177/15563316251341321. Online ahead of print. HSS J. 2025. PMID: 40458230 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous