High prevalence of reverse transcriptase inhibitors associated resistance mutations among people living with HIV on dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy in Francistown, Botswana
- PMID: 39764689
- PMCID: PMC11879200
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkae472
High prevalence of reverse transcriptase inhibitors associated resistance mutations among people living with HIV on dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy in Francistown, Botswana
Abstract
Objectives: We assessed HIV-1 drug resistance profiles among people living with HIV (PLWH) with detectable viral load (VL) and on dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy (ART) in Botswana.
Methods: The study utilised available 100 residual HIV-1 VL samples from unique PLWH in Francistown who had viraemia at-least 6 months after initiating ART in Botswana's national ART program from November 2023 to January 2024. Viraemia was categorized as low-level viraemia (LLV) (VL: 200-999 copies/mL) or virologic failure (VF) (VL ≥1000 copies/mL). HIV-1 protease, reverse transcriptase and integrase genes were sequenced using an in-house next-generation sequencing Oxford nanopore technology. HIV-1 drug resistance mutations (DRMs) were identified using the HIVdb Program in the Stanford HIV drug resistance database and compared between VL groups.
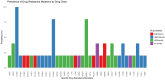
Results: Among 100 participants, 83.0% were on dolutegravir-based, 10.0% were on non-dolutegravir-based ART and 7.0% had unknown/undocumented ART regimens. Thirty (30%) participants had LLV and 70 (70%) had VF. Among 58 successfully sequenced, 32.8% [95% Confidence Interval (CI): 21.8-46.0] had DRMs to any drug class, 33.3% (4/12) in the LLV group and 32.6% (15/46) in the VF group. Among individuals on dolutegravir-based ART, the overall HIV DRMs were 34.8% (95% CI: 22.7-49.2). By VL groups, 40.0% (95% CI: 16.8-68.7) and 33.3% (95% CI: 20.2-50.0) had DRMs at LLV and VF, respectively.
Conclusions: A high but similar prevalence of any DRMs was observed among individuals with LLV and those with VF on dolutegravir-based therapy. Monitoring DRMs in individuals with detectable VL is crucial for preserving dolutegravir-based ART.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- MOH . Botswana Integrated HIV Clinical Care Guidelines, Ministry of Health Botswana. 2016. https://www.moh.gov.bw/Publications/Handbook_HIV_treatment_guidelines.pdf
-
- DHHS . Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1 infected adults and adolescents, Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents, Department of Human and Health Services. 2016. https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/guidelines/documents/ad...
-
- EACS . European AIDS Clinical Society Guidelines. 2021. https://www.eacsociety.org/media/final2021eacsguidelinesv11.0_oct2021.pdf
-
- BHIVA . Guidelines on antiretroviral treatment for adults living with HIV-1 2022, British HIV Association (2023 interim update). 2023. https://www.bhiva.org/file/63513a1745ea9/BHIVA-guidelines-on-antiretrovi...
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K24 AI131928/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- African Academy of Sciences
- U41 HG006941/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- D43 TW009610/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- NIH K24 AI131928/US National Institutes of Health
- Human Health and Heredity in Africa Consortium
- African Academy of Science
- EDCTP2 program
- CSA2020NoE-3104/European Union
- H3ABioNet
- K43 TW012350/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- Sub-Saharan African Network for TB/HIV Research Excellence
- INV-033558/GATES/Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation/United States
- Trials of Excellence in Southern Africa
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical