Targeting SETDB1 in cancer and immune regulation: Potential therapeutic strategies in cancer
- PMID: 39764697
- PMCID: PMC11924802
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12933
Targeting SETDB1 in cancer and immune regulation: Potential therapeutic strategies in cancer
Abstract
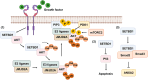
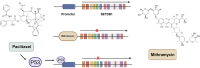
SET domain bifurcated histone lysine methyltransferase 1 (SETDB1/ESET), a pivotal H3K9 methyltransferase, has been extensively studied since its discovery over two decades ago. SETDB1 plays critical roles in immune regulation, including B cell maturation, T-cell activity modulation, and endogenous retrovirus (ERV) silencing. While essential for normal immune cell function, SETDB1 overexpression in cancer cells disrupts immune responses by suppressing tumor immunogenicity and facilitating immune evasion. This is achieved through the repression of anti-tumor immune cell production, ERV silencing, and interference with the type I interferon pathway leading to inhibiting immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) efficacy. Beyond its immunological implications, SETDB1 overexpression fosters tumor growth and metastasis via transcriptional silencing of tumor suppressor genes through histone regulation and activating oncogenic signaling by non-histone regulation. These multifaceted roles make SETDB1 an attractive epigenetic target for novel cancer therapies. This review explores SETDB1's dual function in immune regulation and tumor progression, emphasizing its potential in the development of innovative cancer treatments targeting epigenetic dysregulation and oncogenic signaling.
Keywords: SETDB1; cancer; endogenous retrovirus silencing; immune checkpoint blockage; methyltransferase.
© 2025 The Author(s). The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
H.K.L. is a consultant for Stablix, Inc. All other authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Eames HL, Saliba DG, Krausgruber T, Lanfrancotti A, Ryzhakov G, Udalova IA. KAP1/TRIM28: an inhibitor of IRF5 function in inflammatory macrophages. Immunobiology. 2012;217(12):1315–1324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

