Comparison of Ultrasound Characteristics of Peripapillary Hyperreflective Ovoid Mass-Like Structures and Optic Disc Drusen in Children
- PMID: 39764848
- PMCID: PMC12068547
- DOI: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000002299
Comparison of Ultrasound Characteristics of Peripapillary Hyperreflective Ovoid Mass-Like Structures and Optic Disc Drusen in Children
Abstract
Background: In children, pseudopapilledema is frequently caused by peripapillary hyperreflective ovoid mass-like structures (PHOMS) or optic disc drusen (ODD). While enhanced depth imaging (EDI) OCT can identify both, lack of cooperation, especially from younger children due to the duration of testing, often necessitates the use of B-scan ultrasound (BSUS). This study investigated whether PHOMS are hyperreflective on BSUS and if BSUS can differentiate PHOMS from ODD.
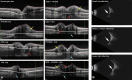
Methods: Pediatric patients referred by a neuro-ophthalmologist to the diagnostic ultrasound clinic for optic nerve head elevation between March 2019 and May 2021 were eligible. Subjects who underwent BSUS and EDI-OCT and were diagnosed with pseudopapilledema based on examination, imaging findings, stability on follow-up, and, in some cases, normal CSF opening pressure were included. ODD were identified on EDI-OCT as structures above the lamina cribrosa with a hyporeflective core and hyperreflective margin prominent superiorly. Hyperreflective horizontal lines (HHL) above the lamina cribrosa without ODD were identified. PHOMS were defined as ovoid, hyperreflective structures above Bruch's membrane external to the optic disc, with similar reflectivity to the retinal nerve fiber layer on OCT and upward deflection of other retinal layers. The BSUSs were read by a separate, masked evaluator who graded the size and reflectivity.
Results: Two hundred thirty-nine eyes (120 patients; 58.3% female; mean age = 11.6 years) with pseudopapilledema were included. EDI-OCT mostly demonstrated PHOMS only (58.1%), followed by PHOMS and HHL (12.6%), and then PHOMS and ODD (11.7%). A combination of PHOMS, ODD, and HHL was found in 8.8%, 1.7% had HHL only, 0.8% had ODD and HHL, and 0.4% had ODD only. 5.9% of eyes were normal on OCT. On BSUS, 78.4% of eyes with only PHOMS demonstrated low or intermediate reflectivity, while 92.9% of eyes with both PHOMS and ODD demonstrated high reflectivity. When HHL was present with or without other findings, a majority demonstrated high reflectivity.
Conclusions: Though PHOMS are hyperreflective on BSUS, ODD are more highly reflective, which may allow clinicians to differentiate between the two if EDI-OCT is unavailable. Eyes with both PHOMS and HHL have similar characteristics to those with ODD, supporting current theories that these lines may be early indicators of evolving drusen.
Copyright © 2025 by North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Behrens CM, Malmqvist L, Jørgensen M, et al. Peripapillary hyperreflective ovoid mass–like structures (PHOMS) in children: the Copenhagen child cohort 2000 eye study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2023;245:212–221. - PubMed
-
- Malmqvist L, Li XQ, Eckmann CL, et al. Optic disc drusen in children: the Copenhagen child cohort 2000 eye study. J Neuroophthalmol. 2018;38:140–146. - PubMed
-
- Malmqvist L, Li XQ, Hansen MH, et al. Progression over 5 years of prelaminar hyperreflective lines to optic disc drusen in the Copenhagen child cohort 2000 eye study. J Neuroophthalmol. 2020;40:315–321. - PubMed
-
- Malmqvist L, Bursztyn L, Costello F, et al. The optic disc drusen studies consortium recommendations for diagnosis of optic disc drusen using optical coherence tomography. J Neuroophthalmol. 2018;38:299–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

