Transforaminal Lumbar Endoscopic Discectomy: A Novel Alternative for Management of Lumbar Disc Herniation in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- PMID: 39765266
- PMCID: PMC11744524
- DOI: 10.14245/ns.2448634.317
Transforaminal Lumbar Endoscopic Discectomy: A Novel Alternative for Management of Lumbar Disc Herniation in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Abstract
Objective: Lumbar disc herniation (LDH) represents an increasingly encountered condition in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The aim of the present study is to assess the progress of health-related quality of life following transforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy (TELD) for LDH in patients suffering from RA.
Methods: Seventy-four patients, scheduled to undergo elective TELD for LDH, were prospectively enrolled in the study. Group A included 36 otherwise healthy individuals and group B 38 patients complementarily diagnosed with RA according to the 2010 ACR/EULAR (American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism) criteria. The Medical Outcomes Study 36-item Short Form health survey (SF-36) was selected for the outcome assessment at baseline and postoperatively, at selected intervals at 6 weeks, 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively.
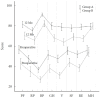
Results: Group A presented statistically significantly higher scores in all SF-36 domains and all selected intervals (p<0.001), except for mental health parameter. All aspects of SF-36 questionnaire significantly improved postoperatively (p<0.001) and in each group independently. Nevertheless, the absolute improvement between consecutive time intervals did not differ significantly between the 2 groups.
Conclusion: Patients diagnosed with RA who undergo TELD for LDH demonstrate statistically significant improvement in their health status, as measured by SF-36 questionnaire, one year after the procedure. This improvement is comparable with normal individuals.
Keywords: Lumbar disc herniation; Minimally invasive spine surgery; Quality of life; Rheumatoid arthritis; Transforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Joaquim AF, Appenzeller S. Cervical spine involvement in rheumatoid arthritis--a systematic review. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:1195–202. - PubMed
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–81. - PubMed
-
- Bland J, Davis P, London M, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis of cervical spine. Arch Intern Med. 1963;112:892–8. - PubMed
-
- Heywood AW, Meyers OL. Rheumatoid arthritis of the thoracic and lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68:362–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

