Senescent brain cell types in Alzheimer's disease: Pathological mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
- PMID: 39765417
- PMCID: PMC12047392
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00519
Senescent brain cell types in Alzheimer's disease: Pathological mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Abstract
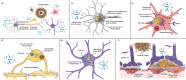
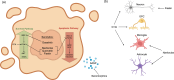
Cellular senescence is a cell state triggered by programmed physiological processes or cellular stress responses. Stress-induced senescent cells often acquire pathogenic traits, including a toxic secretome and resistance to apoptosis. When pathogenic senescent cells form faster than they are cleared by the immune system, they accumulate in tissues throughout the body and contribute to age-related diseases, including neurodegeneration. This review highlights evidence of pathogenic senescent cells in the brain and their role in Alzheimer's disease (AD), the leading cause of dementia in older adults. We also discuss the progress and challenges of senotherapies, pharmacological strategies to clear senescent cells or mitigate their toxic effects, which hold promise as interventions for AD and related dementias (ADRD).
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Biology of aging; Neurescence; Neurodegeneration; tau.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest MEO has a patent pending, ‘Detecting and Treating Conditions Associated with Neuronal Senescence. The other authors declare no competing interests in relation to this work.
Figures
References
-
- Lopez-Otin C., Blasco M.A., Partridge L., Serrano M., Kroemer G. Hallmarks of aging: an expanding universe. Cell. 2023;186(2):243–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

