Computed Tomography-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Nasal Carcinomas in Dogs
- PMID: 39765586
- PMCID: PMC11672759
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14243682
Computed Tomography-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Nasal Carcinomas in Dogs
Abstract
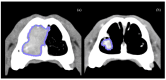
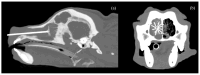
Nasal carcinomas in dogs are locally invasive neoplasms with a low metastatic rate that pose significant treatment challenges due to their location and aggressiveness. This study evaluates the safety, feasibility, and therapeutic outcomes of computed tomography-guided radiofrequency ablation (CT-guided RFA) in 15 dogs diagnosed with nasal adenocarcinoma. All patients underwent staging and histopathological diagnosis before treatment. CT-guided RFA achieved a significant tumor volume reduction (82.8%) and improvement in clinical signs such as nasal discharge, epistaxis, and respiratory distress, without complications. Post-RFA CT examinations demonstrated a significant decrease in Hounsfield units and tumor volume. This study has shown that CT-guided RFA is an effective cytoreductive option for minimally invasive management of nasal adenocarcinomas in dogs, particularly when traditional therapies like radiation therapy or surgery are not feasible.
Keywords: CT-guided procedure; cancer therapy; canine; diagnostic imaging; minimally invasive therapy; nasal carcinoma; radiofrequency ablation; thermoablation; veterinary oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
María Dolores Alférez and Pablo Gómez-Ochoa are employees of VetCorner Unavets, and Telmo Fernandes is an employee of Imaginologia Veterinaria do Porto, which provided radiofrequency ablation services. The other authors have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Adams W.M., Kleiter M.M., Thrall D.E., Klauer J.M., Forrest L.J., La Due T.A., Havighurst T.C. Prognostic significance of tumor histology and computed tomographic staging for radiation treatment response of canine nasal tumors. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. 2009;50:330–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1740-8261.2009.01545.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

