Duguetia furfuracea (A.ST. Hil.) Saff.: Neuroprotective Effect on Chemically Induced Amnesia, Anxiolytic Effects and Preclinical Safety Evaluation in Mice
- PMID: 39765648
- PMCID: PMC11726886
- DOI: 10.3390/biology13120981
Duguetia furfuracea (A.ST. Hil.) Saff.: Neuroprotective Effect on Chemically Induced Amnesia, Anxiolytic Effects and Preclinical Safety Evaluation in Mice
Abstract
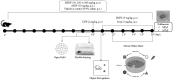
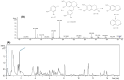
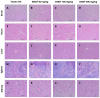
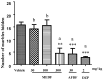
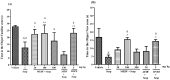
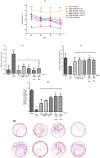
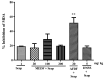
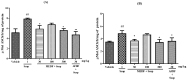
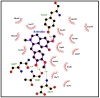
Duguetia furfuracea, "araticum-seco", is known to contain several bioactive compounds that can mitigate oxidative stress and act on the central nervous system (CNS). This effect is partly attributed to its potent antioxidant and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors. In this study, the effects were explored of the methanolic extract (MEDF) and alkaloid fraction (AFDF) of D. furfuracea (leaves) on cognitive behaviors in male mice with scopolamine (Scop)-induced cognitive impairment and biochemical parameters. Additionally, anxiolytic behavior, subacute toxicity, molecular docking and antioxidant activity were reported. MEDF (30, 100 or 300 mg/kg) or AFDF (30 mg/kg) were orally administered for 16 days and Scop (intraperitoneally, i.p.) between days 11 and 16. The anxiolytic behavior (open field test and marble burying) in healthy mice, and the Scop-induced memory impairment (object recognition test and Morris water maze (MWM)) were assessed, and the biochemical parameters (malondialdehyde (MDA) and AChE levels) were measured after euthanasia. The subacute toxicological impact of MEDF was assessed in female Swiss mice for 28 days. MEDF and AFDF were available for the DPPH, ABTS and β-carotene/linoleic acid models. The results revealed that MEDF and AFDF exhibit anxiolytic effects and significantly alleviated Sco-induced memory impairment, inhibited AChE in the cortex (40%) and MDA (51.51%) levels. Reticuline was reported in AFDF and molecular coupling with AChE involves link-type hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions. MEDF exhibited antioxidant capacity (DPPH, IC50 = 18.10 ± 1.70 µg/mL; ABTS, IC50 = 10.41 ± 1.69 µg/mL). MEDF did not reveal signs of toxicity. In conclusion, D. furfuracea shows promise in mitigating scopolamine-induced memory deficits, potentially because it inhibits AChE activity, reduces MDA levels, and enhances antioxidant activities.
Keywords: AChE; anxiety; dementia; scopolamine; “araticum seco”.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Maas P.J.M., Westra L.Y.T., Chatrou L.W. Duguetia. Flora Neotrop. Monogr. 2003;88:1–274.
-
- Pott A., Pott V.J. Plantas do Pantanal. [(accessed on 15 February 2024)];Embrapa-SPI. 1994 33 Available online: http://www.alice.cnptia.embrapa.br/alice/handle/doc/783791.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

