Safety Evaluation for Acute and Chronic Oral Toxicity of Maha Pigut Triphala Contains Three Medicinal Fruits in Sprague-Dawley Rats
- PMID: 39765672
- PMCID: PMC11673089
- DOI: 10.3390/biology13121005
Safety Evaluation for Acute and Chronic Oral Toxicity of Maha Pigut Triphala Contains Three Medicinal Fruits in Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
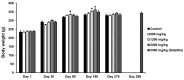
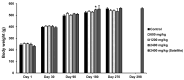
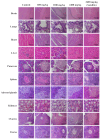
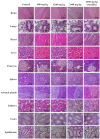
Maha Pigut Triphala is the herbal mixture of three fruits consisting of T. bellirica, T. chebula, and E. officinalis also known as P. emblica. Humans regularly eat the fresh fruits of these plants on a daily basis. Maha Pigut Triphala is one of the widely known herbal medicinal formulas used in traditional Thai medicine. Besides studying pharmacological properties, attention should also be paid to the safety and toxicity studies of herbal medicines. The objective of the present study was to evaluate the acute and chronic oral toxicity of Maha Pigut Triphala (2:1:3) in Sprague-Dawley rats. A single dose of Maha Pigut Triphala at a concentration of 5000 mg/kg body weight was administered orally to female rats in the acute oral toxicity study. In the chronic oral toxicity study, male and female rats were treated with various concentrations of Maha Pigut Triphala (600, 1200, and 2400 mg/kg body weight) once daily for 270 consecutive days. The presence of abnormalities in the symptoms and behavior of the rats were observed and recorded throughout the experiment. Additionally, body weight, organ weight, and mortality were recorded. At the end of the study, blood samples were collected for hematological and blood chemistry analysis, while the internal organs were evaluated for gross pathological and histopathological changes. The acute oral toxicity study revealed no mortality and abnormal symptoms or behavior in Maha Pigut Triphala-treated rats. Moreover, gross pathological and histopathological findings did not reveal any abnormalities in the internal organs. In the chronic oral toxicity evaluation, although there were negligible changes in body weight, organ weight, and hematological and blood chemistry parameters in rats treated with Maha Pigut Triphala for 270 days, no behavioral or gross pathological and histopathological abnormalities were observed. Overall, the results of this study demonstrate that Maha Pigut Triphala (2:1:3) neither causes acute nor chronic oral toxicity in rats, proposing the safety of this herbal formula in animals prior to human trials and use.
Keywords: Emblica officinalis; Maha Pigut Triphala; Phyllanthus emblica; Sprague-Dawley rats; Terminalia bellirica; Terminalia chebula; acute oral toxicity; chronic oral toxicity; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti Bacterial Efficacy of Terminalia Chebula, Terminalia Bellirica, Embilica Officinalis and Triphala on Salivary Streptococcus Mutans Count - A Linear Randomized Cross Over Trial.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Feb;11(2):ZC47-ZC51. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/23558.9355. Epub 2017 Feb 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 28384980 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of the Oral Triphala Recipe from Acute and Chronic Toxicity Tests in Sprague-Dawley Rats.Toxics. 2022 Aug 30;10(9):514. doi: 10.3390/toxics10090514. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36136479 Free PMC article.
-
Triphala in prevention of dental caries and as an antimicrobial in oral cavity- a review.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2015;15(2):89-97. doi: 10.2174/1871526515666150513105009. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25966965 Review.
-
A comprehensive metabolome profiling of Terminalia chebula, Terminalia bellerica, and Phyllanthus emblica to explore the medicinal potential of Triphala.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):31635. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80544-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738152 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific validation of the ethnomedicinal properties of the Ayurvedic drug Triphala: a review.Chin J Integr Med. 2012 Dec;18(12):946-54. doi: 10.1007/s11655-012-1299-x. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Chin J Integr Med. 2012. PMID: 23239004 Review.
References
-
- Thoithoisana Devi S., Devika Chanu K., Singh N.B., Chaudhary S.K., Keithellakpam O.S., Singh K.B., Mukherjee P.K., Sharma N. Chemical Profiling and Therapeutic Evaluation of Standardized Hydroalcoholic Extracts of Terminalia chebula Fruits Collected from Different Locations in Manipur against Colorectal Cancer. Molecules. 2023;28:2901. doi: 10.3390/molecules28072901. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jayesh K., Karishma R., Vysakh A., Gopika P., Latha M.S. Terminalia bellirica (Gaertn.) Roxb fruit exerts anti-inflammatory effect via regulating arachidonic acid pathway and pro-inflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Inflammopharmacology. 2020;28:265–274. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0513-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adane F., Assefa W., Alem M.B., Dessalegn M. Sub-chronic toxicity of the aqueous leaf extract of Ocimum lamiifolium Hochst. ex Benth on biochemical parameters and histopathology of liver and kidney in rats: In vivo and in-silico toxicity studies. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023;23:30. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03863-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- National Library of Thailand . The Book of Medicine Edition Royal King Rama V. The Fine Arts Department; Bangkok, Thailand: 1999.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

