Analysis of the Preventive Effect of Lonicera caerulea Pomace and Its Isolated Components on Colitis in Mice Based on Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolomics
- PMID: 39765807
- PMCID: PMC11672951
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13121478
Analysis of the Preventive Effect of Lonicera caerulea Pomace and Its Isolated Components on Colitis in Mice Based on Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolomics
Abstract
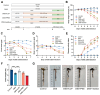
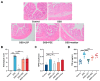
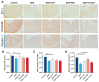
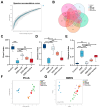
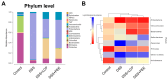
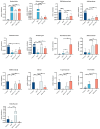
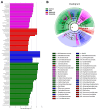
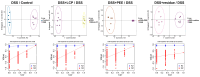
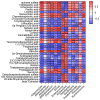
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including relapsing-remitting ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, is a non-specific chronic intestinal inflammatory disease. Lonicera caerulea, which is rich in polyphenolic compounds, has been shown to exert antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. The research evaluates the dietary impacts of Lonicera caerulea pomace, its polyphenol-rich extract, and fiber-rich residue on colitis symptoms. Colitis was induced with 2.5% DSS (dextran sulfate sodium) aqueous solution after continuous feeding of customized Lonicera caerulea feed for 2.5 weeks. The results indicate that the intake of the polyphenol-rich extract has an effect in preventing colitis in mice, but the effect is less than that by the pomace itself, and the fiber residue alone does not prevent the condition when ingested. The pomace and polyphenol-rich extract have a positive regulatory effect on the gut microbiota of mice with colitis, and the intake of Lonicera caerulea pomace significantly restores 15 metabolites in mice with colitis, significantly improving five metabolic pathways, including steroid biosynthesis, with the regulation of metabolites and metabolic pathways being significantly correlated with the gut microbiota.
Keywords: Lonicera caerulea; anti-inflammatory; gut microbiota; metabolomics; polyphenol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

