Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Capacity and Bioavailability of Whey Protein Concentrate-Based Coenzyme Q10 Nanoparticles
- PMID: 39765863
- PMCID: PMC11727553
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13121535
Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Capacity and Bioavailability of Whey Protein Concentrate-Based Coenzyme Q10 Nanoparticles
Abstract
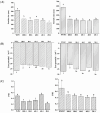
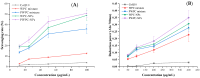
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a powerful antioxidant. However, the poor water solubility and low bioavailability still remain challenges for its application. An embedded delivery system of CoQ10 based on whey protein concentrate (WPC) and polymerized whey protein concentrate (PWPC) was prepared, and the physicochemical properties, antioxidant capacity and bioavailability were characterized in this study. Both groups of nanoparticles showed a particle size distribution from 241 to 331 nm in the protein-to-CoQ10 mass ratio range of 100:1 to 20:1. In addition, the minimum polydispersity index value was observed at the mass ratio of 20:1. Differential scanning calorimetry and Fourier transform infrared spectra analysis revealed that the CoQ10 was successfully dispersed in the WPC and PWPC particles through hydrophobic interaction in both groups in addition to the hydrogen bond present in the WPC group. All nanoparticles exhibited irregular spherical or aggregate structure in the transmission electron microscopy diagram. The PWPC-based nanoparticles showed a slightly higher antioxidant capacity than that of the WPC, and both values were significantly higher than that of its corresponding physical mixture and free CoQ10 (p < 0.05). The results of the simulated gastrointestinal digestion experiments denoted that these two nanoparticles could protect CoQ10 from gastric digestion and then deliver it to the intestine. Compared with its free state, the bioavailability of CoQ10 embedded in WPC and PWPC increased by nearly 7.58 times and 7.48 times, respectively. The data indicated that WPC and PWPC could be effective delivery carriers to enhance the bioavailability of active substances like CoQ10.
Keywords: antioxidant capacity; bioavailability; coenzyme CoQ10; physicochemical properties; whey protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Yubero-Serrano E.M., Delgado-Casado N., Delgado-Lista J., Perez-Martinez P., Tasset-Cuevas I., Santos-Gonzalez M., Caballero J., Garcia-Rios A., Marin C., Gutierrez-Mariscal F.M., et al. Postprandial antioxidant effect of the Mediterranean diet supplemented with coenzyme Q10 in elderly men and women. Age. 2011;33:579–590. doi: 10.1007/s11357-010-9199-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- González-Guardia L., Yubero-Serrano E.M., Delgado-Lista J., Perez-Martinez P., Garcia-Rios A., Marin C., Camargo A., Delgado-Casado N., Roche H.M., Perez-Jimenez F., et al. Effects of the Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with coenzyme Q10 on metabolomic profiles in elderly men and women. J. Gerontol. A Biol. 2015;70:78–84. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glu098. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dumont M., Kipiani K., Yu F.M., Wille E., Katz M., Calingasan N.Y., Gouras G.K., Lin M.T., Beal M.F. Coenzyme Q10 decreases amyloid pathology and improves behavior in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011;27:211–223. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-110209. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakhshayeshkaram M., Lankarani K.B., Mirhosseini N., Tabrizi R., Akbari M., Dabbaghmanesh M.H., Asemi Z. The effects of Coenzyme Q10 supplementation on metabolic profiles of patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018;24:3710–3723. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666181112112857. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

