Prevalence of Maternal Anemia in Southern Jordan: Findings from a Cross-Sectional Study and 5-Year Review
- PMID: 39765922
- PMCID: PMC11727851
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12242495
Prevalence of Maternal Anemia in Southern Jordan: Findings from a Cross-Sectional Study and 5-Year Review
Abstract
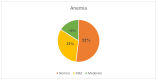
Background: The literature underrepresents maternal anemia in southern Jordan, and national studies often have small sample sizes. According to the 2019 Jordan National Micronutrient Survey, maternal anemia in Jordan accounted for 19.1% of cases, with the majority experiencing mild anemia (17.1%). Among the 29 pregnant women recruited from the southern region, 56.5% had anemia, of which 34.8% had mild and 21.7% had moderate anemia. The current study provides an update on the prevalence of anemia during pregnancy in southern Jordan. Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted at a government referral hospital in southern Jordan. Pregnant women who visited outpatient clinics were included in the study. Data were collected through face-to-face interviews, and blood samples were collected to measure hemoglobin levels. Descriptive analyses of continuous and categorical variables were performed. Maternal anemia risk factors were assessed using the chi-square test, Fisher's exact test, and multivariate logistic regression analysis. Statistical significance was defined at p < 0.05. Results: Of the 474 pregnant women who agreed to participate, 36.8% had anemia. Education, income, diet (number of meals and meat consumption), regularity of antenatal care, and supplement use were factors that significantly affected hemoglobin levels (p < 0.05). The adolescent pregnancy rate was 5.3%, and 48% had mild to moderate anemia. Conclusions: Maternal anemia rates in southern Jordan remained high, despite a slow decline. Reducing this burden requires improved access to healthcare and health education, particularly for rural residents who are at greater risk of disease.
Keywords: Jordan; adolescent pregnancy; anemia; antenatal care; maternal health; pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors certify that there are no conflicts of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Current Trends CDC Criteria for Anemia in Children and Childbearing-Aged Women. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1990;144:151–152. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1990.02150260029019. - DOI
-
- Stevens G.A., Finucane M.M., De-Regil L.M., Paciorek C.J., Flaxman S.R., Branca F., Peña-Rosas J.P., Bhutta Z.A., Ezzati M., Nutrition Impact Model Study Group (Anaemia) Global, regional, and national Trends in haemoglobin concentration and prevalence of total and severe anaemia in children and pregnant and non-pregnant women for 1995–2011: A systematic analysis of population-representative data. Lancet Glob. Health. 2013;1:e16–e25. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70001-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Young M.F., Oaks B.M., Rogers H.P., Tandon S., Martorell R., Dewey K.G., Wendt A.S. Maternal low and high hemoglobin concentrations and associations with adverse maternal and infant health outcomes: An updated global systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023;23:264. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-05489-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Indicator Group Details. [(accessed on 27 July 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/indicator-groups/indicat....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources