Evaluation of the Epidemiological Disease Burden and Nationwide Cost of Endometriosis in Hungary
- PMID: 39765994
- PMCID: PMC11675645
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12242567
Evaluation of the Epidemiological Disease Burden and Nationwide Cost of Endometriosis in Hungary
Abstract
Background: Endometriosis is one of the most common gynecological diseases that can lead to infertility. The aim of this quantitative, descriptive, and cross-sectional study was to analyze the prevalence and the annual nationwide health insurance treatment cost of endometriosis in Hungary in 2010 and 2019.
Methods: The data used in this study were sourced from publicly funded, national, real-world datasets administered by the National Health Insurance Administration (NHIFA). The total number of cases of endometriosis in the Hungarian population was determined by ICD codes and all types of care. The total prevalence, age-specific prevalence, and annual health insurance expenditure by age group were evaluated.
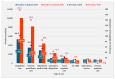
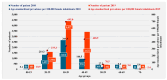
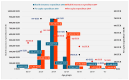
Results: The highest numbers of patients and prevalence (2010: 101.9/100,000 women; 2019: 197.3/100,000 women) were found in outpatient care. Endometriosis, regardless of its type, mainly affects patients in the 30-39-year age group (number of patients-2010: 6852; 2019: 11,821). The NHIFA spent a total of EUR 1,639,612 on endometriosis treatment in 2010 and EUR 1,905,476 in 2019. The average annual health insurance expenditure per capita was EUR 574 in 2010 and EUR 426 in 2019. There was a significant correlation between length of stay and mean age of patients in both years (2010 r = 0.856, p < 0.001; 2019 r = 0.877, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The number endometriosis cases is increasing. Early diagnosis and targeted treatment would reduce endometriosis symptoms and therefore improve patients' quality of life and reduce health insurance costs. This would be helped by the establishment of endometriosis centers.
Keywords: age-standardized prevalence; cost of illness; economic burden; endometriosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and Annual Health Insurance Cost of Endometriosis in Hungary-A Nationwide Study Based on Routinely Collected, Real-World Health Insurance Claims Data.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 May 16;11(10):1448. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11101448. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239734 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological disease burden and annual, nationwide health insurance treatment cost of female infertility based on real-world health insurance claims data in Hungary.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Mar 4;25(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-12348-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 40038705 Free PMC article.
-
Annual epidemiological and health insurance disease burden of hip osteoarthritis in Hungary based on nationwide data.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 May 23;25(1):406. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07513-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38783258 Free PMC article.
-
Economic Implications of Endometriosis: A Review.Pharmacoeconomics. 2022 Dec;40(12):1143-1158. doi: 10.1007/s40273-022-01211-0. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Pharmacoeconomics. 2022. PMID: 36344867 Review.
-
The Economic Impact of Smoking and of Reducing Smoking Prevalence: Review of Evidence.Tob Use Insights. 2015 Jul 14;8:1-35. doi: 10.4137/TUI.S15628. eCollection 2015. Tob Use Insights. 2015. PMID: 26242225 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

