Perceived Health Needs, Social Support, and Depression Among Patients with Myocardial Infarction: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 39765997
- PMCID: PMC11727848
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12242570
Perceived Health Needs, Social Support, and Depression Among Patients with Myocardial Infarction: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of mortality globally. Myocardial infarction (MI), a major type of cardiovascular disease, presents long-term challenges for patients. Recognizing patients' perceived health needs and the factors that influence them is crucial for providing comprehensive care and improving outcomes.
Aim: This paper explores the perceived health needs, levels of depression, and social support among MI patients, as well as investigates the correlations between these factors.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted at King Salman Specialist Hospital from March to June 2024, enrolling 244 MI patients through convenience sampling. Data collection was performed using the following three validated questionnaires: the Cardiac Patient Learning Needs Inventory (CPLNI) to assess the learning needs of MI patients, the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) to evaluate depression levels, and the Oslo Social Support Scale (OSSS-3) to measure social support. Statistical analysis was carried out using IBM SPSS Statistics, Version 27.
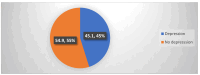
Results: Patients aged 40 years or older and those who were employed exhibited greater learning needs (p < 0.001). Female patients were more depressed than males (p = 0.008). Higher social support was reported by the female patients, those with a family history of MI, and those who were employed (p = 0.002, 0.002, and 0.003, respectively). The total mean score for perceived learning needs was 3.72, with the highest needs in "other pertinent information", "medication information", and "anatomy and physiology". Depression was indicated in 45.1% of MI patients, with significantly higher depression levels in female than in male patients. Additionally, a significant positive correlation was found between social support and perceived learning needs (r = 0.205, p = 0.001), as well as a negative correlation between social support and depression (r = -0.441, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Addressing both the physical and psychological needs is essential for MI patients. Comprehensive educational programs and mental health support services are necessary for improving outcomes. Personalized patient education and routine depression screenings should be integrated into post-MI care. Future research should examine longitudinal changes in learning needs and mental health status.
Keywords: depression; learning needs; myocardial infarction; social support.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2014. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2014.
-
- Campo G., Tonet E., Chiaranda G., Sella G., Maietti E., Bugani G., Vitali F., Serenelli M., Mazzoni G., Ruggiero R., et al. Exercise intervention improves quality of life in older adults after myocardial infarction: Randomised clinical trial. Heart. 2020;106:1658–1664. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2019-316349. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources