Relative Survival, Conditional Survival, and Causes of Death in Patients with Early Gastric Cancer, with a Focus on Differences Between Cardia and Non-Cardia Cancer
- PMID: 39766160
- PMCID: PMC11674421
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16244262
Relative Survival, Conditional Survival, and Causes of Death in Patients with Early Gastric Cancer, with a Focus on Differences Between Cardia and Non-Cardia Cancer
Abstract
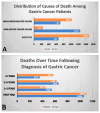
Background: Many researchers believe that cardia (CGC) and non-cardia (NCGC) are two different types of tumors, having different features like incidence rate, risk factors, geographical location, and socioeconomic status. This study aims to investigate the causes of death (COD) survival rates among early gastric cancer patients with a focus on differences between CGC and NCGC. Methods: This retrospective study employed SEER*stat software (version 8.3.92) to analyze the SEER 17 plus dataset (2000-2019). Standardized mortality ratios (SMR) were computed. Relative survival and conditional survival post-diagnosis were calculated using R software (version 4.1.0) among the different subgroups. Results: Within the follow-up period, 55.4% (5381) died, predominantly within the initial year post-diagnosis. Esophageal cancer was the leading non-gastric cancer cause in CGC, while miscellaneous tumors dominated in NCGC. The 1-year and 5-year relative survival for CGC patients were 76.4% and 48.9% respectively, while for NCGC were 80.4% and 63.9%. The 3-year conditional survival after 1 year and 5e years of survival for CGC were 68.7% and 88.8%, respectively, while for NCGC were 82.2% and 93.5%, respectively. This means that the longer a person has survived after diagnosis with cancer, the greater the likelihood that person will survive for another 3 years. Conclusions: This study sheds light on the substantial impact of non-cancer COD in GC patients, underscoring the necessity of considering comorbidities in their comprehensive management and follow-up. Impact: This study contributes valuable insights for clinical decision-making and informs future research directions regarding CGC and NCGC.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; SEER; causes of death; epidemiology; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in preparing this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Global patterns of cardia and non-cardia gastric cancer incidence in 2012.Gut. 2015 Dec;64(12):1881-8. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308915. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Gut. 2015. PMID: 25748648
-
Developing a prognostic signature: identifying differentially expressed genes in cardia and non-cardia gastric cancer for immunity and therapeutic sensitivity analysis.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Aug 31;15(4):1446-1463. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-541. Epub 2024 Aug 28. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39279940 Free PMC article.
-
The Distinct Impact of TAM Infiltration on the Prognosis of Patients With Cardia and Non-Cardia Gastric Cancer and Its Association With H. pylori Infection.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 3;11:737061. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.737061. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34926251 Free PMC article.
-
20-Year Comparative Survival and Mortality of Cancer of the Stomach by Age, Sex, Race, Stage, Grade, Cohort Entry Time-Period, Disease Duration & Selected ICD-O-3 Oncologic Phenotypes: A Systematic Review of 157,258 Cases for Diagnosis Years 1973-2014: (SEER*Stat 8.3.4).J Insur Med. 2019;48(1):5-23. doi: 10.17849/insm-48-1-1-19.1. Epub 2019 Oct 14. J Insur Med. 2019. PMID: 31609640
-
Cancer of the Larynx-20-Year Comparative Survival and Mortality Analysis by Age, Sex, Race, Stage, Grade, Cohort Entry Time-Period, Disease Duration and ICD-O-3 Topographic Primary Sites-Codes C32.0-9: A Systematic Review of 43,103 Cases for Diagnosis Years 1975-2017: (NCI SEER*Stat 8.3.9).J Insur Med. 2024 Jul 1;51(2):92-110. doi: 10.17849/insm-51-2-92-110.1. J Insur Med. 2024. PMID: 39266004
References
-
- Wang X., Liu F., Li Y., Tang S., Zhang Y., Chen Y., Khan S.A. Comparison on Clinicopathological Features, Treatments and Prognosis between Proximal Gastric Cancer and Distal Gastric Cancer: A National Cancer Data Base Analysis. J. Cancer. 2019;10:3145–3153. doi: 10.7150/jca.30371. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Isik A., Okan I., Firat D., Yilmaz B., Akcakaya A., Sahin M. A new prognostic strategy for gastric carcinoma: Albumin level and metastatic lymph node ratio. Minerva Chir. 2014;69:147–153. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

