Structure and Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Complex
- PMID: 39766194
- PMCID: PMC11673145
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14121488
Structure and Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Complex
Abstract
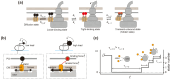
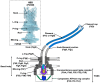
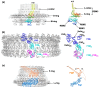
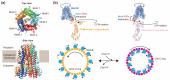
Many bacteria swim in liquids and move over solid surfaces by rotating flagella. The bacterial flagellum is a supramolecular protein complex that is composed of about 30 different flagellar proteins ranging from a few to tens of thousands. Despite structural and functional diversities of the flagella among motile bacteria, the flagellum commonly consists of a membrane-embedded rotary motor fueled by an ion motive force across the cytoplasmic membrane, a universal joint, and a helical propeller that extends several micrometers beyond the cell surface. The flagellar motor consists of a rotor and several stator units, each of which acts as a transmembrane ion channel complex that converts the ion flux through the channel into the mechanical work required for force generation. The rotor ring complex is equipped with a reversible gear that is regulated by chemotactic signal transduction pathways. As a result, bacteria can move to more desirable locations in response to environmental changes. Recent high-resolution structural analyses of flagella using cryo-electron microscopy have provided deep insights into the assembly, rotation, and directional switching mechanisms of the flagellar motor complex. In this review article, we describe the current understanding of the structure and dynamics of the bacterial flagellum.
Keywords: bacterial flagellum; chemotaxis; cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM); motility; proton motive force; rotor; stator; torque generation; transmembrane proton channel complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural basis of torque generation in the bi-directional bacterial flagellar motor.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Feb;47(2):160-172. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.06.005. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 34294545 Review.
-
Architecture and Assembly of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Complex.Subcell Biochem. 2021;96:297-321. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58971-4_8. Subcell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33252734 Review.
-
Flagella-Driven Motility of Bacteria.Biomolecules. 2019 Jul 14;9(7):279. doi: 10.3390/biom9070279. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31337100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and Function of Stator Units of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor.Cell. 2020 Oct 1;183(1):244-257.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.016. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32931735
-
In Situ Structure of the Vibrio Polar Flagellum Reveals a Distinct Outer Membrane Complex and Its Specific Interaction with the Stator.J Bacteriol. 2020 Jan 29;202(4):e00592-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00592-19. Print 2020 Jan 29. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 31767780 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for assembly and function of the Salmonella flagellar MS-ring with three different symmetries.Commun Biol. 2025 Jan 16;8(1):61. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07485-2. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39820129 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Analysis of Transcriptomes and Metabolomes Reveals Key Genes and Substances That Affect the Formation of a Multi-Species Biofilm by Nine Gut Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2025 Jan 22;13(2):234. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020234. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005603 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-Scale Video Imaging of Motility Machinery by High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 10;15(2):257. doi: 10.3390/biom15020257. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Does the Archaellum Work?Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 21;15(4):465. doi: 10.3390/biom15040465. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305169 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

