Is Hemopexin a Nephrotoxin or a Marker of Kidney Injury in Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion?
- PMID: 39766229
- PMCID: PMC11673696
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14121522
Is Hemopexin a Nephrotoxin or a Marker of Kidney Injury in Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion?
Abstract
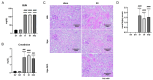
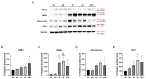
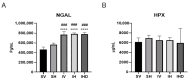
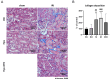
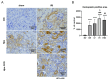
Destabilization of heme proteins is recognized to play a role in acute kidney injury (AKI). Hemopexin (Hpx), known for its role in binding heme, mitigates free heme toxicity. Despite this, the potential adverse effects of Hpx deposition in kidney tissues and its impact on kidney function are not fully understood. Deferoxamine (DFO) chelates iron released from heme and mitigates associated kidney damage. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate whether Hpx contributes to kidney injury in an ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) induced AKI model and to investigate if DFO could alleviate this damage. Mice were categorized into five groups: Sham-Vehicle, Sham-Hpx, IRI-Vehicle, IRI-Hpx, and IRI-Hpx-DFO. Decline in kidney function was observed exclusively in the IRI group, independent of Hpx injection. Serum Hpx levels remained comparable across all groups, and administration of Hpx did not alter serum Hpx levels or kidney function after 24 hours. Although increased Hpx deposition in kidneys was noted in both the IRI and Hpx groups, this accumulation did not correlate with impaired kidney function. Additionally, DFO did not exhibit a protective effect against kidney injury. In summary, Hpx does not directly induce kidney injury and cannot be considered a biomarker for kidney damage caused by IRI.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; biomarker; hemopexin; ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Liu K.D., Goldstein S.L., Vijayan A., Parikh C.R., Kashani K., Okusa M.D., Agarwal A., Cerda J., AKI!Now Initiative of the American Society of Nephrology AKI!Now Initiative: Recommendations for Awareness, Recognition, and Management of AKI. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020;15:1838–1847. doi: 10.2215/CJN.15611219. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

