The Physiological Functions and Therapeutic Potential of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α in Vascular Calcification
- PMID: 39766299
- PMCID: PMC11674127
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14121592
The Physiological Functions and Therapeutic Potential of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α in Vascular Calcification
Abstract
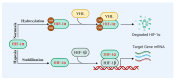
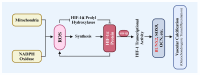
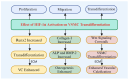
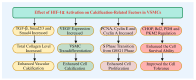
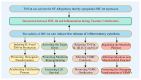
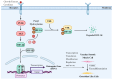
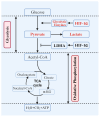
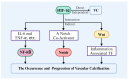
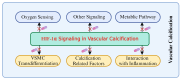
HIF-1α plays a crucial regulatory role in vascular calcification (VC), primarily influencing the osteogenic differentiation of VSMCs through oxygen-sensing mechanisms. Under hypoxic conditions, the stability of HIF-1α increases, avoiding PHD and VHL protein-mediated degradation, which promotes its accumulation in cells and then activates gene expressions related to calcification. Additionally, HIF-1α modulates the metabolic state of VSMCs by regulating the pathways that govern the switch between glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation, thereby further advancing the calcification process. The interaction between HIF-1α and other signaling pathways, such as nuclear factor-κB, Notch, and Wnt/β-catenin, creates a complex regulatory network that serves as a critical driving force in VC. Therefore, a deeper understanding of the role and regulatory mechanism of the HIF-1α signaling during the development and progression of VC is of great significance, as it is not only a key molecular marker for understanding the pathological mechanisms of VC but also represents a promising target for future anti-calcification therapies.
Keywords: energy metabolism; hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; therapeutic target; vascular calcification; vascular smooth muscle cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

