Regulation of Vascular Injury and Repair by P21-Activated Kinase 1 and P21-Activated Kinase 2: Therapeutic Potential and Challenges
- PMID: 39766303
- PMCID: PMC11674331
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14121596
Regulation of Vascular Injury and Repair by P21-Activated Kinase 1 and P21-Activated Kinase 2: Therapeutic Potential and Challenges
Abstract
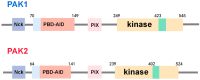
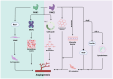
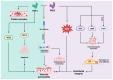
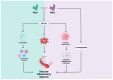
The PAK (p21-activated kinases) family is a class of intracellular signal transduction protein kinases that regulate various cellular functions, mainly through their interactions with small GTP enzymes. PAK1 and PAK2 in the PAK kinase family are key signal transduction molecules that play important roles in various biological processes, including morphological changes, migration, proliferation, and apoptosis, and are involved in the progression of many diseases. Abnormal expression or dysregulation of PAK1 and PAK2 may be associated with several diseases, including cancer, neurological diseases, etc. The current research mainly focuses on studying the role of PAK and PAK inhibitors in the regulation of cancer progression, but relatively few reports are available that explore their potential role in cardiovascular diseases. Vascular injury and repair are complex processes involved in many cardiovascular conditions, including atherosclerosis, restenosis, and hypertension. Emerging research suggests that PAK1 and PAK2 have pivotal roles in vascular endothelial cell functions, including migration, proliferation, and angiogenesis. These kinases also modulate vascular smooth muscle relaxation, vascular permeability, and structural alterations, which are critical in the development of atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation. By targeting these activities, PAK proteins are essential for both normal vascular physiology and the pathogenesis of vascular diseases, highlighting their potential as therapeutic targets for vascular health. This review focuses on recent studies that offer experimental insights into the mechanisms by which PAK1 and PAK2 regulate the biological processes of vascular injury and repair and the therapeutic potential of the current existing PAK inhibitors in vascular-related diseases. The limitations of treatment with some PAK inhibitors and the ways that future development can overcome these challenges are also discussed.
Keywords: P21-activated kinase; angiogenesis; inflammation; signaling pathway; vascular permeability; vascular remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
P21-activated kinase in inflammatory and cardiovascular disease.Cell Signal. 2014 Sep;26(9):2060-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.04.020. Epub 2014 May 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24794532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p21-Activated Kinase 2 Regulates Endothelial Development and Function through the Bmk1/Erk5 Pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Dec;35(23):3990-4005. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00630-15. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26391956 Free PMC article.
-
PAK1, PAK1Δ15, and PAK2: similarities, differences and mutual interactions.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 20;9(1):17171. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53665-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31748572 Free PMC article.
-
PAK2 as a therapeutic target in cancer: Mechanisms, challenges, and future perspectives.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025 Feb;1880(1):189246. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189246. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39694422 Review.
-
Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake partly relies on p21-activated kinase (PAK)2, but not PAK1, in mouse skeletal muscle.J Physiol. 2020 Dec;598(23):5351-5377. doi: 10.1113/JP280294. Epub 2020 Sep 17. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32844438 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PPP1R12B inhibits cell proliferation by inducing G0/G1 phase arrest via PAK2/β-catenin axis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 19;13:1621705. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1621705. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40612101 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

