UPLC-MS/MS High-Risk Screening for Sphingolipidoses Using Dried Urine Spots
- PMID: 39766319
- PMCID: PMC11727146
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14121612
UPLC-MS/MS High-Risk Screening for Sphingolipidoses Using Dried Urine Spots
Abstract
Background: Early detection of sphingolipidoses is crucial to prevent irreversible complications and improve patient outcomes. The use of urine samples dried on filter paper (DUS) is a non-invasive strategy that simplifies the collection, storage, and shipping of samples compared to using liquid urine specimens.
Objectives: (1) Develop and validate a multiplex ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) methodology using DUS to quantify twenty-one lysosphingolipids normalized to creatinine for eight different sphingolipidoses. (2) Establish normal reference values to evaluate the clinical utility of the methodology.
Methods: Samples were eluted from a 5 cm filter paper disk (~1 mL of urine) and extracted on Oasis MCX solid-phase extraction cartridges prior to injection in the UPLC-MS/MS system.
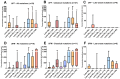
Results: Urinary lysosphingolipids were stable on DUS at -80 °C and -30 °C for 117 days, at 21.5 °C and 4 °C for at least 26 days, and at 35 °C for 3 days. Globotriaosylsphingosine, glucosylsphingosine, and their analogs were elevated in patients with Fabry disease and Gaucher disease, respectively, compared to controls (p-value < 0.0001). The analysis of related analog profiles suggests a better overall reliability in detecting patients early, especially for Fabry patients.
Conclusions: This approach is feasible and might be useful for the early detection, monitoring, and follow-up of patients with sphingolipidoses.
Keywords: Fabry disease; Gaucher disease; lysosomal storage disorders; lysosphingolipids; sphingolipidoses; tandem mass spectrometry; urine dried on filter paper.
Conflict of interest statement
T.M. received a doctoral educational bursary from Sanofi Canada. B.M. declares no conflicts of interest. C. Auray-Blais has received grants, and speaker honoraria from Takeda Pharmaceutical International AG., Sanofi Genzyme, BioMarin Pharmaceuticals Inc., Protalix Biotherapeutics, Amicus Therapeutics, and Avrobio, and traveling expenses from Waters Corp. for lectures given. She has received service agreements from Moderna Therapeutics, Sigilon Therapeutics, and 4D Molecular Therapeutics. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Plasma and dried blood spot lysosphingolipids for the diagnosis of different sphingolipidoses: a comparative study.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2019 Nov 26;57(12):1863-1874. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2018-1301. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 31091195
-
Lysosphingolipid urine screening test using mass spectrometry for the early detection of lysosomal storage disorders.Bioanalysis. 2022 Mar;14(5):289-306. doi: 10.4155/bio-2021-0259. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Bioanalysis. 2022. PMID: 35118880
-
Diagnosis of sphingolipidoses: a new simultaneous measurement of lysosphingolipids by LC-MS/MS.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017 Mar 1;55(3):403-414. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2016-0340. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017. PMID: 27533120
-
Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Sphingolipids: Applications for Diagnosis of Sphingolipidoses.Adv Clin Chem. 2016;77:177-219. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2016.06.004. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Adv Clin Chem. 2016. PMID: 27717417 Review.
-
Sphingolipidoses in Morocco: Chemical profiling for an affordable and rapid diagnosis strategy.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2023 Oct;168:106751. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2023.106751. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2023. PMID: 37295489 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

