Cytokine Gene Variants as Predisposing Factors for the Development and Progression of Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39766338
- PMCID: PMC11726869
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14121631
Cytokine Gene Variants as Predisposing Factors for the Development and Progression of Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most prevalent form of cardiovascular disease. A growing body of research shows that interleukins (ILs), such as IL-8, IL-18 and IL-16, elicit pro-inflammatory responses and may play critical roles in the pathologic process of CAD. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), capable of generating functional modifications in IL genes, appear to be associated with CAD risk. This study aims to evaluate the associations of ten previously identified SNPs of the three cytokines with susceptibility to or protection of CAD. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted using Pubmed, EMBASE, WOS, CENTRAL, CNKI, CBM, Weipu, WANFANG Data and Google Scholar databases for relevant literature published up to September 2024. Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated for the four genetic models of the investigated SNPs in overall and subgroups analyses. Thirty-eight articles from 16 countries involving 14574 cases and 13001 controls were included. The present meta-analysis revealed no significant association between CAD and IL-8-rs2227306 or five IL-16 SNPs (rs8034928, rs3848180, rs1131445, rs4778889 and rs11556218). However, IL-8-rs4073 was significantly associated with an increased risk of CAD across all genetic models. In contrast, three IL-18 (rs187238, rs1946518 and rs1946519) variants containing minor alleles were associated with decreased risks of CAD under all models. Subgroups analyses by ethnicity indicated that IL-8-rs4073 conferred a significantly higher risk of CAD among Asians, including East, South and West Asians (allelic OR = 1.46, homozygous OR = 1.96, heterozygous OR = 1.47, dominant OR = 1.65), while it showed an inversely significant association with CAD risk in Caucasians (homozygous OR = 0.82, dominant OR = 0.85). Additionally, IL-18-rs187238 and IL-18-rs1946518 were significantly associated with reduced CAD risks in East Asians (for rs187238: allelic OR = 0.72, homozygous OR = 0.33, heterozygous OR = 0.73, dominant OR = 0.71; for rs1946518: allelic OR = 0.62, homozygous OR = 0.38, heterozygous OR = 0.49, dominant OR = 0.45). IL-18-rs187238 also demonstrated protective effects in Middle Eastern populations (allelic OR = 0.76, homozygous OR = 0.63, heterozygous OR = 0.72, dominant OR = 0.71). No significant associations were observed in South Asians or Caucasians for these IL-18 SNPs. Consistent with the overall analysis results, subgroups analyses further highlighted a significant association between IL-8-rs4073 and increased risk of acute coronary syndrome (heterozygous OR = 0.72). IL-18-rs187238 was significantly associated with decreased risks of myocardial infarction (MI) (allelic OR = 0.81, homozygous OR = 0.55, dominant OR = 0.80) and multiple vessel stenosis (allelic OR = 0.54, heterozygous OR = 0.45, dominant OR = 0.45). Similarly, IL-18-rs1946518 was significantly associated with reduced MI risk (allelic OR = 0.75, heterozygous OR = 0.68). These findings support the role of cytokine gene IL-8 and IL-18 variants as predisposing factors for the development and progression of CAD.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; cytokine variants; meta-analysis; predisposing factors; pro-inflammatory response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
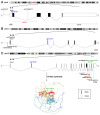
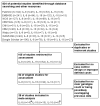
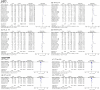
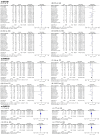


References
-
- Disease G.B.D., Injury I., Prevalence C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1545–1602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mortality G.B.D., Causes of Death C. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1459–1544. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Diseases G.B.D., Injuries C. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 2024;403:2133–2161. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

