Gut Microbiota Modulation: A Novel Strategy for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy
- PMID: 39766360
- PMCID: PMC11674688
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14121653
Gut Microbiota Modulation: A Novel Strategy for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy
Abstract
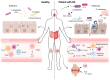
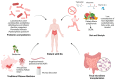
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that leads to joint inflammation, progressive tissue damage and significant disability, severely impacting patients' quality of life. While the exact mechanisms underlying RA remain elusive, growing evidence suggests a strong link between intestinal microbiota dysbiosis and the disease's development and progression. Differences in microbial composition between healthy individuals and RA patients point to the role of gut microbiota in modulating immune responses and promoting inflammation. Therapies targeting microbiota restoration have demonstrated promise in improving treatment efficacy, enhancing patient outcomes and slowing disease progression. However, the complex interplay between gut microbiota and autoimmune pathways in RA requires further investigation to establish causative relationships and mechanisms. Here, we review the current understanding of the gut microbiota's role in RA pathogenesis and its potential as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: bacterial metabolites; bacterial translocation; dysbiosis; gut microbiota; molecular mimicry; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- van der Woude D., Alemayehu W.G., Verduijn W., de Vries R.R., Houwing-Duistermaat J.J., Huizinga T.W., Toes R.E. Gene-environment interaction influences the reactivity of autoantibodies to citrullinated antigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:814–816. doi: 10.1038/ng1010-814. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van der Helm-van Mil A.H.M., Wesoly J.Z., Huizinga T.W.J. Understanding the genetic contribution to rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2005;17:299–304. doi: 10.1097/01.bor.0000160780.13012.be. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

