In Vivo and Computational Studies on Sitagliptin's Neuroprotective Role in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications for Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 39766390
- PMCID: PMC11674309
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci14121191
In Vivo and Computational Studies on Sitagliptin's Neuroprotective Role in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications for Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background/objectives: Diabetes mellitus (DM), a widespread endocrine disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, can cause nerve damage and increase the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). Effective blood glucose management is essential, and sitagliptin (SITG), a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, may offer neuroprotective benefits in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: T2DM was induced in rats using nicotinamide (NICO) and streptozotocin (STZ), and biomarkers of AD and DM-linked enzymes, inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis were evaluated in the brain. Computational studies supported the in vivo findings.
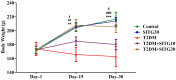
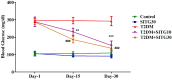
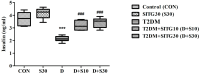
Results: SITG significantly reduced the brain enzyme levels of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), beta-secretase-1 (BACE-1), DPP-4, and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) in T2DM-induced rats. It also reduced inflammation by lowering cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). Additionally, SITG improved oxidative stress markers by reducing malondialdehyde (MDA) and enhancing glutathione (GSH). It increased anti-apoptotic B-cell lymphoma protein-2 (Bcl-2) while reducing pro-apoptotic markers such as Bcl-2-associated X (BAX) and Caspace-3. SITG also lowered blood glucose levels and improved plasma insulin levels. To explore potential molecular level mechanisms, docking was performed on AChE, COX-2, GSK-3β, BACE-1, and Caspace-3. The potential binding affinity of SITG for the above-mentioned target enzymes were 10.8, 8.0, 9.7, 7.7, and 7.9 kcal/mol, respectively, comparable to co-crystallized ligands. Further binding mode analysis of the lowest energy conformation revealed interactions with the critical residues.
Conclusions: These findings highlight SITG's neuroprotective molecular targets in T2DM-associated neurodegeneration and its potential as a therapeutic approach for AD, warranting further clinical investigations.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; apoptosis; brain enzymes; inflammation; molecular docking; oxidative stress; sitagliptin; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Diabetes as a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease in the Middle East and its shared pathological mediators.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020 Feb;27(2):736-750. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.12.028. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32210695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sertraline as a Multi-Target Modulator of AChE, COX-2, BACE-1, and GSK-3β: Computational and In Vivo Studies.Molecules. 2024 Nov 14;29(22):5354. doi: 10.3390/molecules29225354. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39598743 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of bergenin in Alzheimer's disease: Investigation through molecular docking, in vitro and in vivo studies.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Jan 1;356:18-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.08.010. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30118774
-
Neuroprotective Role of DPP-4 Inhibitor Linagliptin Against Neurodegeneration, Neuronal Insulin Resistance and Neuroinflammation Induced by Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin in Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Neurochem Res. 2023 Sep;48(9):2714-2730. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03924-w. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 37079222
-
Clinical efficacies, underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of Chinese medicines for diabetic nephropathy treatment and management.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Sep;11(9):2749-2767. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.020. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34589395 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Behavioral and histological study on the neuroprotective effect of thymoquinone on the cerebellum in AlCl3-induced neurotoxicity in rats through modulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy.J Mol Histol. 2025 Feb 6;56(2):81. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10361-2. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 39912993
-
Incretin-Based Therapies in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease: Advancing Neuroprotection With Dual and Triple Agonists-A Review.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 15;8(7):e71065. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.71065. eCollection 2025 Jul. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40671844 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jarrar M., Abusalah M.A.H., Albaker W., Al-Bsheish M., Alsyouf A., Al-Mugheed K., Issa M.R., Alumran A. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the general population of Saudi Arabia, 2000–2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 2023;11:1–10. doi: 10.4103/sjmms.sjmms_394_22. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baduini I.R., Castro Vildosola J.E., Kavehmoghaddam S., Kiliç F., Nadeem S.A., Nizama J.J., Rowand M.A., Annapureddy D., Bryan C.A., Do L.H., et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and neurodegenerative disorders: The mitochondrial connection. Pharmacol. Res. 2024;209:107439. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107439. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

