Dental Antimicrobial Stewardship: Developing a Mobile Application for Rational Antibiotic Prescribing to Tackle Misdiagnosis
- PMID: 39766525
- PMCID: PMC11672394
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13121135
Dental Antimicrobial Stewardship: Developing a Mobile Application for Rational Antibiotic Prescribing to Tackle Misdiagnosis
Abstract
Background/objectives: Inexperienced dentists and dental students are especially prone to misdiagnosis, and this represents a huge problem regarding antimicrobial stewardship. We aimed to develop a mobile app for rational antibiotic prescribing in dentistry based on local-systemic symptoms and patient factors, rather than solely on diagnosis, to tackle misdiagnosis.
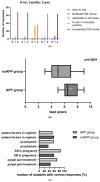
Methods: The study involved 64 participants, 50 of which were third-year dental students attending a pharmacology course focusing on antimicrobials, comprising lectures and practical sessions without (noAPP group, n = 22) or with (APP group n = 28) the assistance of a mobile application. The other 14 participants were practicing dentists who decided to register and use the application. All registered users of the application were asked to take a feedback survey, while learning outcomes were evaluated via a pharmacology quiz.
Results: A decision tree was used for application development. In total, 76 impressions were collected on the application. The majority of the impressions were related to odontogenic-endodontic infections. Multiple linear regression analysis did not reveal differences in survey responses between practicing dentists and undergraduate students in the feedback survey responses. There was a significant difference in the mean pharmacology test scores between the noAPP and APP groups (5.50 ± 1.80 vs. 7.21 ± 1.03, p = 0.0001).
Conclusions: The dentalantibiotic.com application was developed to support rational antibiotic prescribing, in view of tackling misdiagnosis, among inexperienced dentists, as well as to assist in undergraduates' pharmacology learning, and the current study shows its large impact as an educational tool. The majority of participants considered it easy to use, efficient in facilitating the right antibiotic choice, and useful for everyday decision-making.
Keywords: antimicrobial stewardship; dentistry; misdiagnosis; mobile application.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Stefan Djordjević was employed by IMP-Computer Systems Ltd. (IMP-CS). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
How decisions are made: Antibiotic stewardship in dentistry.Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2023 Nov;44(11):1731-1736. doi: 10.1017/ice.2023.173. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 37553682 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Antibiotic Prescribing Is Underpinned by Dental Ethics Principles: Survey on Postgraduate and Undergraduate Dental Students' Perceptions.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 May 17;13(5):460. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13050460. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786188 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a clinical decision support tool for the management of traumatic dental injuries in the primary dentition by novice and expert clinicians.Dent Traumatol. 2018 Apr;34(2):120-128. doi: 10.1111/edt.12390. Dent Traumatol. 2018. PMID: 29476702
-
Towards Wiser Prescribing of Antibiotics in Dental Practice: What Pharmacists Want Dentists to Know.Dent J (Basel). 2024 Oct 29;12(11):345. doi: 10.3390/dj12110345. Dent J (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39590395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
International Consensus on a Dental Antibiotic Stewardship Core Outcome Set.Int Dent J. 2023 Jun;73(3):456-462. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2023.03.006. Epub 2023 Apr 12. Int Dent J. 2023. PMID: 37055238 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wilson W.R., Gewitz M., Lockhart P.B., Bolger A.F., DeSimone D.C., Kazi D.S., Couper D.J., Beaton A., Kilmartin C., Miro J.M., et al. Prevention of Viridans Group Streptococcal Infective Endocarditis: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143:e963–e978. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000969. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lockhart P.B., Tampi M.P., Abt E., Aminoshariae A., Durkin M.J., Fouad A.F., Gopal P., Hatten B.W., Kennedy E., Lang M.S., et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline on antibiotic use for the urgent management of pulpal- and periapical-related dental pain and intraoral swelling: A report from the American Dental Association. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2019;150:906–921.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2019.08.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

