Dairy Cattle and the Iconic Autochthonous Cattle in Northern Portugal Are Reservoirs of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli
- PMID: 39766598
- PMCID: PMC11672626
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13121208
Dairy Cattle and the Iconic Autochthonous Cattle in Northern Portugal Are Reservoirs of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli
Abstract
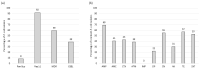
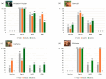
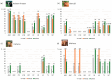
Background/Objectives: Animals destined for human consumption play a key role in potentially transmitting bacteria carrying antibiotic resistance genes. However, there is limited knowledge about the carriage of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in native breeds. We aimed to characterize the phenotypic profiles and antibiotic resistance genes in Escherichia coli isolated from bovines, including three native Portuguese bovine breeds. Methods: Forty-nine E. coli isolates were selected from 640 fecal samples pooled by age group (eight adult or eight calf samples) from each farm, representing both dairy cattle raised in intensive systems and meat cattle raised in extensive systems in Northern Portugal. The presumptive E. coli colonies plated onto MacConkey agar were confirmed using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). The antibiotic resistance profiles were screened by antimicrobial susceptibility testing (EUCAST/CLSI guidelines), and the antibiotic resistance genes by PCR. Results: Most isolates showed resistance to ampicillin (69%), tetracycline (57%), gentamicin (55%), and trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole (53%), with no resistance to imipenem. Resistance to at least one antibiotic was found in 92% of isolates, while 59% exhibited multidrug resistance. Most calf isolates, including those from native breeds, showed a multidrug-resistant phenotype. Among the adults, this was only observed in Holstein-Friesian and Barrosã cattle. None of the Holstein-Friesian isolates were susceptible to all the tested antibiotics. ESBL-producing E. coli was identified in 39% of isolates, including those from Holstein-Friesian calves and adults, Cachena calves and Minhota adults. The sul2 gene was detected in 69% of isolates, followed by blaCTX-M (45%), aac(3')-IV (41%), and aac(6')-Ib-cr (31%), with a higher prevalence in adults. Conclusions: This pioneering study highlights the concerning presence of multidrug-resistant E. coli in native Portuguese cattle breeds.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; One Health; antimicrobial resistance; livestock; native breeds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ma F., Xu S., Tang Z., Li Z., Zhang L. Use of Antimicrobials in Food Animals and Impact of Transmission of Antimicrobial Resistance on Humans. Biosaf. Health. 2021;3:32–38. doi: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2020.09.004. - DOI
-
- FAO. UNEP. WHO. WOAH . One Health Joint Plan of Action (2022–2026): Working Together for the Health of Humans, Animals, Plants and the Environment. WHO; Rome, Italy: 2022. - DOI
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) European Medicines Agency (EMA) Antimicrobial consumption and resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals: Fourth joint inter-agency report on integrated analysis of antimicrobial agent consumption and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals in the EU/EEA JIACRA IV—2019–2021. EFSA J. Eur. Food Saf. Auth. 2024;22:e8589. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2024.8589. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

