Bacterial Infections, Trends, and Resistance Patterns in the Time of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Romania-A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39766609
- PMCID: PMC11726834
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13121219
Bacterial Infections, Trends, and Resistance Patterns in the Time of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Romania-A Systematic Review
Abstract
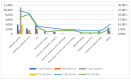
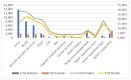
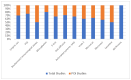
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has intensified concerns over bacterial infections and antimicrobial resistance, particularly in Romania. This systematic review explores bacterial infection patterns and resistance during the pandemic to address critical gaps in knowledge. Methods: A systematic review, following PRISMA guidelines, was conducted using databases such as PubMed and Scopus, focusing on studies of bacterial infections from 2020 to 2022. Articles on bacterial infections in Romanian patients during the pandemic were analyzed for demographic data, bacterial trends, and resistance profiles. Results: A total of 87 studies were included, detailing over 20,000 cases of bacterial infections. The review found that Gram-negative bacteria, particularly Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae, were the most frequently identified pathogens, alongside Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus spp. Multidrug resistance (MDR) was noted in 24% of the reported strains, with common resistance to carbapenems and cephalosporins. Conclusions: The pandemic has amplified the complexity of managing bacterial infections, particularly in critically ill patients. The rise in MDR bacteria underscores the need for stringent antimicrobial stewardship and infection control measures. Continuous monitoring of bacterial trends and resistance profiles will be essential to improve treatment strategies in post-pandemic healthcare settings.
Keywords: COVID-19; Romania; bacterial; coinfection; pandemic; phenotype; resistance; superinfection; trends.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Leretter M., Vulcanescu D., Horhat F., Matichescu A., Rivis M., Rusu L.-C., Roi A., Racea R., Badea I., Dehelean C., et al. COVID-19: Main findings after a year and half of unease and the proper scientific progress (Review) Exp. Ther. Med. 2022;23:424. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11350. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vulcănescu M.I., Vlaicu L., Bălăuţă D., Jivanov G. Loneliness and Social Isolation of the Elderly from Drobeta-Turnu Severin during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Soc. Work. Rev. 2021;1:149–158.
-
- Goian C., Vlaicu L., Moţăţeanu G., Bălăuţă D., Popovici C. The Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Children with Special Educational Needs in Rural Areas from Mehedinţi County. Soc. Work. Rev. 2022;1:95–103.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous