Goondicones A-H: Spiro-Isoindolinone Heartworm Anthelmintics from an Australian Pasture-Soil-Derived Streptomyces sp
- PMID: 39766612
- PMCID: PMC11727212
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13121222
Goondicones A-H: Spiro-Isoindolinone Heartworm Anthelmintics from an Australian Pasture-Soil-Derived Streptomyces sp
Abstract
Background/objectives: There is an urgent need for new and improved anthelmintics that are not constrained by existing resistance pathways and that can safeguard the health and welfare of animals.
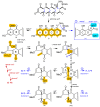
Methods: An integrated platform of chemical, bioassay, and cultivation profiling applied to a library of microbes isolated from Australian livestock pasture soil was used to detect and guide the production, isolation, characterization, identification, and evaluation of new natural products with anthelmintic properties.
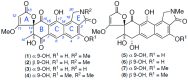
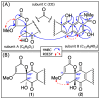
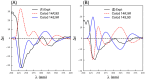
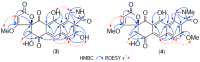
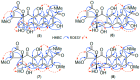
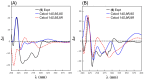
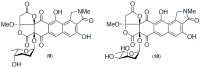
Results: A global natural products social (GNPS) molecular network analysis of 110 Australian pasture-soil-derived microbial extracts prioritized for antiparasitic activity identified unique molecular families in the extract of Streptomyces sp. S4S-00185A06, a strain selectively active against Dirofilaria immitis microfilariae. UPLC-DAD analysis identified metabolites with unique UV-vis chromophores and unprecedented molecular formulas. A chemical investigation of Streptomyces sp. S4S-00185A06 yielded goondicones A-H (1-8) as new examples of a rare class of spiro-isoindolinones, with structures assigned on the basis of detailed spectroscopic analysis, ECD calculations, and biosynthetic considerations.
Conclusions: While goondicones 1-8 exhibit little to no in vitro inhibitory activity against Gram-positive, Gram-negative, and/or fungal pathogens, human carcinoma cells, or the livestock gastrointestinal parasite Haemonchus contortus L1-L3 larvae, 5 and 6 (and, to a lesser extent, 1) inhibit the motility of heartworm Dirofilaria immitis microfilaria (IC50 10-11 μM). A structure activity relationship analysis based on the co-metabolites 1-8 suggests that (i) an 8-OH is preferable to 8-oxo moiety, (ii) 20-NMe and 3-OH moieties are essential, and (iii) C-9 epimerization exerts no discernible impact on in vitro potency.
Keywords: Dirofilaria immitis; Soils for Science; Streptomyces; anthelmintic; citizen science; microbial natural product; spiro-isoindolinone.
Conflict of interest statement
David Bruhn, Cynthia Childs, and Yovany Moreno are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health, USA Inc. All remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

