Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Effect of Clove and Thyme Essential Oils on Growth Inhibition and Biofilm Formation of Arcobacter spp. and Other Bacteria
- PMID: 39766622
- PMCID: PMC11672449
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13121232
Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Effect of Clove and Thyme Essential Oils on Growth Inhibition and Biofilm Formation of Arcobacter spp. and Other Bacteria
Abstract
Background: In recent years, significant resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics has been observed. A biofilm is a structure that significantly aids the survival of the microbial population and also significantly affects its resistance. Methods: Thyme and clove essential oils (EOs) were subjected to chemical analysis using gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector (GC-FID). Furthermore, the antimicrobial effect of these EOs was tested in both the liquid and vapor phases using the volatilization method. The effect of the EOs on growth parameters was monitored using an RTS-8 bioreactor. However, the effect of the EOs on the biofilm formation of commonly occurring bacteria with pathogenic potential was also monitored, but for less described and yet clinically important strains of Arcobacter spp. Results: In total, 37 and 28 compounds were identified in the thyme and clove EO samples, respectively. The most common were terpenes and also derivatives of phenolic substances. Both EOs exhibited antimicrobial activity in the liquid and/or vapor phase against at least some strains. The determined antimicrobial activity of thyme and clove oil was in the range of 32-1024 µg/mL in the liquid phase and 512-1024 µg/mL in the vapor phase, respectively. The results of the antimicrobial effect are also supported by similar conclusions from monitoring growth curves using the RTS bioreactor. The effect of EOs on biofilm formation differed between strains. Biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was completely suppressed in an environment with a thyme EO concentration of 1024 µg/mL. On the other hand, increased biofilm formation was found, e.g., in an environment of low concentration (1-32 µg/mL). Conclusions: The potential of using natural matrices as antimicrobials or preservatives is evident. The effect of these EOs on biofilm formation, especially Arcobacter strains, is described for the first time.
Keywords: Arcobacter; antimicrobial effect; biofilm formation; clove; essential oil; thyme.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
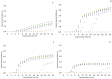
 negative control;
negative control;  positive control;
positive control;  32 µg/mL;
32 µg/mL;  64 µg/mL;
64 µg/mL;  128 µg/mL;
128 µg/mL;  256 µg/mL;
256 µg/mL;  512 µg/mL;
512 µg/mL;  1024 µg/mL.
1024 µg/mL.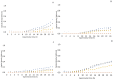
 negative control;
negative control;  positive control;
positive control;  32 µg/mL;
32 µg/mL;  64 µg/mL;
64 µg/mL;  128 µg/mL;
128 µg/mL;  256 µg/mL;
256 µg/mL;  512 µg/mL;
512 µg/mL;  1024 µg/mL.
1024 µg/mL.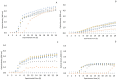
 negative control;
negative control;  positive control;
positive control;  32 µg/mL;
32 µg/mL;  64 µg/mL;
64 µg/mL;  128 µg/mL;
128 µg/mL;  256 µg/mL;
256 µg/mL;  512 µg/mL;
512 µg/mL;  1024 µg/mL.
1024 µg/mL.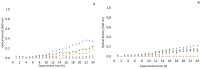
 negative control;
negative control;  positive control;
positive control;  32 µg/mL;
32 µg/mL;  64 µg/mL;
64 µg/mL;  128 µg/mL;
128 µg/mL;  256 µg/mL;
256 µg/mL;  512 µg/mL;
512 µg/mL;  1024 µg/mL.
1024 µg/mL.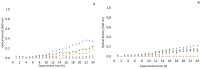
 negative control;
negative control;  positive control;
positive control;  32 µg/mL;
32 µg/mL;  64 µg/mL;
64 µg/mL;  128 µg/mL;
128 µg/mL;  256 µg/mL;
256 µg/mL;  512 µg/mL;
512 µg/mL;  1024 µg/mL.
1024 µg/mL.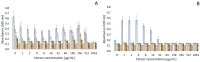
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa CCM 1961, Arcobacter butzleri CCUG 30484;
Pseudomonas aeruginosa CCM 1961, Arcobacter butzleri CCUG 30484;  Staphylococcus aureus CCM 4223, Arcobacter cryaerophilus CCM 7050;
Staphylococcus aureus CCM 4223, Arcobacter cryaerophilus CCM 7050;  Enterococcus faecalis CCM 4224, Arcobacter skirrowii LMG 6621;
Enterococcus faecalis CCM 4224, Arcobacter skirrowii LMG 6621;  Escherichia coli CCM 2024, Arcobacter defluvii LMG 25694;
Escherichia coli CCM 2024, Arcobacter defluvii LMG 25694;  positive control.
positive control.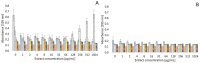
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa CCM 1961, Arcobacter butzleri CCUG 30484;
Pseudomonas aeruginosa CCM 1961, Arcobacter butzleri CCUG 30484;  Staphylococcus aureus CCM 4223, Arcobacter cryaerophilus CCM 7050;
Staphylococcus aureus CCM 4223, Arcobacter cryaerophilus CCM 7050;  Enterococcus faecalis CCM 4224, Arcobacter skirrowii LMG 6621;
Enterococcus faecalis CCM 4224, Arcobacter skirrowii LMG 6621;  Escherichia coli CCM 2024, Arcobacter defluvii LMG 25694;
Escherichia coli CCM 2024, Arcobacter defluvii LMG 25694;  positive control.
positive control.Similar articles
-
Antibacterial activity evaluation of selected essential oils in liquid and vapor phase on respiratory tract pathogens.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jul 27;18(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2291-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 30053847 Free PMC article.
-
Vapor-phase activities of cinnamon, thyme, and oregano essential oils and key constituents against foodborne microorganisms.J Agric Food Chem. 2007 May 30;55(11):4348-56. doi: 10.1021/jf063295u. Epub 2007 May 8. J Agric Food Chem. 2007. PMID: 17488023
-
Validation of Qualitative Broth Volatilization Checkerboard Method for Testing of Essential Oils: Dual-Column GC-FID/MS Analysis and In Vitro Combinatory Antimicrobial Effect of Origanum vulgare and Thymus vulgaris against Staphylococcus aureus in Liquid and Vapor Phases.Plants (Basel). 2021 Feb 18;10(2):393. doi: 10.3390/plants10020393. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670756 Free PMC article.
-
Novel strategies of essential oils, chitosan, and nano- chitosan for inhibition of multi-drug resistant: E. coli O157:H7 and Listeria monocytogenes.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Apr;29(4):2582-2590. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.12.036. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35531141 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Oils as Antimicrobial Agents-Myth or Real Alternative?Molecules. 2019 Jun 5;24(11):2130. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112130. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31195752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aromatic Herbs as a Source of Bioactive Compounds: An Overview of Their Antioxidant Capacity, Antimicrobial Activity, and Major Applications.Molecules. 2025 Mar 14;30(6):1304. doi: 10.3390/molecules30061304. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40142079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

