Impact of Haemoadsorption Therapy on Short Term Mortality and Vasopressor Dependency in Severe Septic Shock with Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 39766623
- PMCID: PMC11672687
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13121233
Impact of Haemoadsorption Therapy on Short Term Mortality and Vasopressor Dependency in Severe Septic Shock with Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
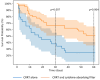
Background/Objectives: Sepsis, a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection, remains a major challenge in ICUs. This study evaluated whether combining haemoadsorption therapy with continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) reduces ICU and short-term mortality in patients with severe septic shock and acute kidney injury (AKI) requiring CRRT. Methods: A single-centre retrospective cohort study was conducted at Rambam Health Care Campus, Haifa, Israel, from January 2018 to February 2024. Data were collected from ICU patients with severe septic shock and AKI requiring CRRT. Patients were divided into two groups: those receiving haemoadsorption therapy with CRRT and those receiving CRRT alone. Primary and secondary endpoints included ICU, 30 and 60-day mortality, vasopressor dependency index (VDI), and lactate levels. Results: Out of 545 patients with septic shock, 133 developed AKI requiring CRRT, and 76 met the inclusion criteria. The haemoadsorption group (n = 47) showed significant reductions in blood lactate levels and VDI after 24 h compared to the CRRT alone group (n = 29). ICU mortality was significantly lower in the haemoadsorption group (34.0% vs. 65.5%, p = 0.008), as was 30 and 60-day mortality (34.0% vs. 62.1%, p = 0.02, and 48.9% vs. 75.9%, p = 0.002). Multivariate analysis confirmed haemoadsorption therapy as independently associated with lower ICU and 30-day but not 60-day mortality. Conclusions: Haemoadsorption therapy combined with CRRT in patients with severe septic shock and AKI requiring CRRT is associated with improved lactate clearance, reduced vasopressor requirements, and lower ICU and 30-day mortality. Further high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm these findings.
Keywords: Cytosorb; Oxiris; acute kidney injury; continuous renal replacement therapy; cytokine removal; haemoadsorption; septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adsorption therapy in critically ill with septic shock and acute kidney injury: a retrospective and prospective cohort study.Ann Intensive Care. 2020 Nov 18;10(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s13613-020-00772-7. Ann Intensive Care. 2020. PMID: 33206229 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy With Adsorbing Filter oXiris in Acute Kidney Injury With Septic Shock: A Retrospective Observational Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 8;9:789623. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.789623. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35463014 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Extracorporeal Blood Purification Therapy using Double Haemoadsorption Device in Severe Endotoxin Septic Shock: A Case Report.J Crit Care Med (Targu Mures). 2022 Nov 12;8(4):292-295. doi: 10.2478/jccm-2022-0028. eCollection 2022 Oct. J Crit Care Med (Targu Mures). 2022. PMID: 36474615 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of continuous renal replacement therapy in patients with septic AKI: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Aug;98(33):e16800. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016800. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31415389 Free PMC article.
-
Hemoadsorption in the Management of Septic Shock: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 27;14(7):2285. doi: 10.3390/jcm14072285. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40217734 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fatal Influenza B-MRSA Coinfection in a Healthy Adolescent: Necrotizing Pneumonia, Cytokine Storm, and Multi-Organ Failure.Children (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;12(6):766. doi: 10.3390/children12060766. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siew L.Y., Lee Z.-Y., Yunos N.M., Atan R., Cove M.E., Lumlertgul N., Srisawat N., Hasan M.S. Outcomes of Extracorporeal Blood Purification with OXiris® Membrane in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Crit. Care. 2024;83:154844. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2024.154844. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous