Placenta Thickness Mediates the Association Between AKIP1 Methylation in Maternal Peripheral Blood and Full-Term Small for Gestational Age Neonates
- PMID: 39766778
- PMCID: PMC11675766
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15121510
Placenta Thickness Mediates the Association Between AKIP1 Methylation in Maternal Peripheral Blood and Full-Term Small for Gestational Age Neonates
Abstract
Background/objectives: A-kinase-interacting protein 1 (AKIP1) has been discovered to be a pivotal signaling adaptor in the regulation of human labor and associated with preterm birth, but its effect on fetal growth was still unclear. Meanwhile, the regulation role of DNA methylation (DNAm) on placental and fetal development has been demonstrated. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the association of AKIP1 DNAm in maternal peripheral blood with placental development and full-term small for gestational age (FT-SGA) neonates, and to explore whether placenta mediate the association between AKIP1 DNAm and FT-SGA; Methods: This study was a case-control study including 84 FT-SGAs and 84 FT-AGAs derived from the Shenzhen Birth Cohort Study. The DNA methylation analysis of CpG in the target region of the AKIP1 gene was measured by the Sequenom MassARRAY EpiTYPER approach. Multiple-variable logistic and linear regression analyses were used to estimate the association between the DNAm of three validated CpG sites in the AKIP1 gene, placental thickness, and FT-SGA. Mediation analysis was used to examine the mediation effect of placental development on the association between the DNAm of AKIP1 and FT-SGA.
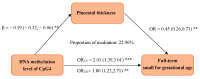
Results: For every increment in standard deviation in the DNAm of CpG4 (cg00061907) at AKIP1, the risk of FT-SGA elevated by 2.01-fold (aOR = 2.01, 95%CI = 1.39~3.01), and the thickness of the placenta significantly decreased by a 0.19 standard deviation (β = -0.19, 95%CI = -0.32~ -0.06). Placental thickness mediated the 22.96% of the effect of the DNAm of CpG4 at AKIP1 on the risk of FT-SGA with statistical significance.
Conclusions: The findings in the present study suggested the mediating effect of placental thickness on the association of the DNAm of AKIP1 in maternal peripheral blood and the risk of FT-SGA, providing new evidence for the mechanism of maternal epigenetics in placental and fetal development.
Keywords: AKIP1; DNA methylation; SGA; mediation effect; placental thickness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Placental surface area mediates the association between FGFR2 methylation in placenta and full-term low birth weight in girls.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Mar 22;10:39. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0472-5. eCollection 2018. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 29588807 Free PMC article.
-
Placenta mediates the association between maternal second-hand smoke exposure during pregnancy and small for gestational age.Placenta. 2015 Aug;36(8):876-80. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 19. Placenta. 2015. PMID: 26051507
-
DNA methylation mediates the effect of maternal smoking on offspring birthweight: a birth cohort study of multi-ethnic US mother-newborn pairs.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Mar 4;13(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01032-6. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 33663600 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Placental Gene Expression in Small-for-Gestational-Age Infants.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jan 10;11(1):80. doi: 10.3390/genes11010080. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31936801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of Placental Biomarkers Predicting Small-for-Gestational-Age Neonates.Biol Res Nurs. 2018 May;20(3):272-283. doi: 10.1177/1099800418760997. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Biol Res Nurs. 2018. PMID: 29490471
References
-
- Lawn J.E., Ohuma E.O., Bradley E., Idueta L.S., Hazel E., Okwaraji Y.B., Erchick D.J., Yargawa J., Katz J., Lee A.C.C., et al. Small babies, big risks: Global estimates of prevalence and mortality for vulnerable newborns to accelerate change and improve counting. Lancet. 2023;401:1707–1719. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00522-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

