Integrative Transcriptomics and Proteomics Analysis Reveals THRSP's Role in Lipid Metabolism
- PMID: 39766829
- PMCID: PMC11675175
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15121562
Integrative Transcriptomics and Proteomics Analysis Reveals THRSP's Role in Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
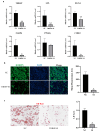
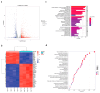
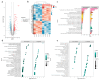
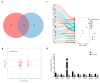
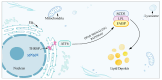
Background/Objectives: Abnormalities in lipid metabolism and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress are strongly associated with the development of a multitude of pathological conditions, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), diabetes mellitus, and obesity. Previous studies have indicated a potential connection between thyroid hormone responsive (THRSP) and lipid metabolism and that ER stress may participate in the synthesis of key regulators of adipogenesis. However, the specific mechanisms remain to be investigated. Methods: In this study, we explored the roles of THRSP in lipid metabolism by interfering with THRSP gene expression in mouse mesenchymal stem cells, comparing the effects on adipogenesis between control and interfered groups, and by combining transcriptomic and proteomic analysis. Results: Our results showed that the number of lipid droplets was significantly reduced after interfering with THRSP, and the expression levels of key regulators of adipogenesis, such as LPL, FABP4, PLIN1, and CIDEC, were significantly downregulated. Both transcriptomic and proteomic results showed that the differential genes (proteins) were enriched in the processes of lipolytic regulation, ER stress, cholesterol metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, PPAR signaling pathway, and glycerophospholipid metabolism. The ER stress marker gene, ATF6, was the most significantly downregulated transcription factor. In addition, RT-qPCR validation indicated that the expression levels of PPAR signaling pathway gene SCD1; key genes of lipid droplet generation including LIPE, DGAT1, and AGPAT2; and ER stress marker gene ATF6 were significantly downregulated. Conclusions: These suggest that THRSP is involved in regulating ER stress and the PPAR signaling pathway, which is closely related to lipid synthesis and metabolism. Interfering with the expression of THRSP may be helpful in ameliorating the occurrence of diseases related to abnormalities in lipid metabolism.
Keywords: THRSP; endoplasmic reticulum stress; lipid metabolism; lipid synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023YFD1300200/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2023BAA029/Major Program (JD) of Hubei Province
- 2022021302024853/Wuhan Science and Technology Major Project on Key Techniques of Biological Breeding and Breeding of New Varieties
- 2022CFB918/Hubei Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021hszd003/Hubei Province science and technology innovation team project, Hubei Hongshan Laboratory Key Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

