Kir4.1 and Aqp4 Contribution to Schisis Cystic Water Accumulation and Clearance in the Rs1 Exon-1 Del XLRS Rat Model
- PMID: 39766850
- PMCID: PMC11675908
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15121583
Kir4.1 and Aqp4 Contribution to Schisis Cystic Water Accumulation and Clearance in the Rs1 Exon-1 Del XLRS Rat Model
Abstract
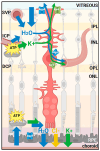
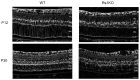
Background/objective: The Rs1 exon-1-del rat (Rs1KO) XLRS model shows normal retinal development until postnatal day 12 (P12) when small cystic spaces start to form in the inner nuclear layer. These spaces enlarge rapidly, peak at P15, and then collapse by P19.
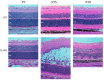
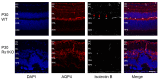
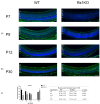
Methods: We explored the possible involvement of Kir4.1 and Aqp4, the principal retina channels for water movement and homeostasis, along with Muller glia cells (MGCs), using semi-quantitative fluorescent immunohistochemistry at P7, P9, P12, and P30, in Rs1KO and WT littermates.
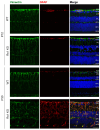
Results: Kir4.1 expression was reduced in Rs1KO retinas at all the early time points-P7, P9, and P12-as the schisis cavities began to form; downregulation would reduce water egress from the retina. Aqp4 was upregulated at P30 in Rs1KO retinas during schisis cavity closure but not as cavities formed at P12. When examined by GFAP expression, MGCs were not activated at the preschisis P12 age but showed considerable GFAP expression at P30 following retinal cystic structural damage at P15, indicating that MGCs were activated during the period of retina water removal and cavity closure.
Conclusions: The study results implicate the downregulation of Kir4.1 in schisis formation and a role for both Kir4.1 and Aqp4 upregulation in subsequent schisis closure.
Keywords: Aqp4; Kir4.1; MGC; Muller glia cells; RS1; X-linked retinoschisis; XLRS; aquaporin4; deep capillary plexus; rat retina disease model; retina development; retinoschisin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dark Rearing Does Not Alter Developmental Retinoschisis Cavity Formation in Rs1 Gene Knockout Rat Model of X-Linked Retinoschisis.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;16(7):815. doi: 10.3390/genes16070815. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40725471 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in aquaporin-4 and Kir4.1 expression in rats with inherited retinal dystrophy.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Jul;148:33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 May 15. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 27191611
-
A developmental switch in the expression of aquaporin-4 and Kir4.1 from horizontal to Müller cells in mouse retina.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Oct;46(10):3869-75. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-0385. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 16186376
-
Of men and mice: Human X-linked retinoschisis and fidelity in mouse modeling.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022 Mar;87:100999. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.100999. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 34390869 Review.
-
Astroglial Kir4.1 and AQP4 Channels: Key Regulators of Potassium Homeostasis and Their Implications in Autism Spectrum Disorders.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun 11;45(1):56. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01574-w. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40498219 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Angle closure glaucoma in a patient with X-linked retinoschisis: a case report.Int J Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar 18;18(3):557-561. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2025.03.24. eCollection 2025. Int J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40103944 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dark Rearing Does Not Alter Developmental Retinoschisis Cavity Formation in Rs1 Gene Knockout Rat Model of X-Linked Retinoschisis.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;16(7):815. doi: 10.3390/genes16070815. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40725471 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

