The Arabidopsis thaliana Double-Stranded RNA Binding Proteins DRB1 and DRB2 Are Required for miR160-Mediated Responses to Exogenous Auxin
- PMID: 39766914
- PMCID: PMC11675975
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15121648
The Arabidopsis thaliana Double-Stranded RNA Binding Proteins DRB1 and DRB2 Are Required for miR160-Mediated Responses to Exogenous Auxin
Abstract
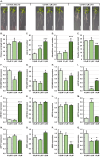
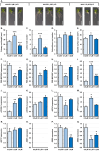
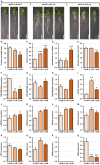
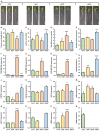
DOUBLE-STRANDED RNA BINDING (DRB) proteins DRB1, DRB2, and DRB4 are essential for microRNA (miRNA) production in Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis) with miR160, and its target genes, AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR10 (ARF10), ARF16, and ARF17, forming an auxin responsive miRNA expression module crucial for root development. Methods: Wild-type Arabidopsis plants (Columbia-0 (Col-0)) and the drb1, drb2, and drb12 mutants were treated with the synthetic auxin 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), and the miR160-mediated response of these four Arabidopsis lines was phenotypically and molecularly characterized. Results: In 2,4-D-treated Col-0, drb1 and drb2 plants, altered miR160 abundance and ARF10, ARF16, and ARF17 gene expression were associated with altered root system development. However, miR160-directed molecular responses to treatment with 2,4-D was largely defective in the drb12 double mutant. In addition, via profiling of molecular components of the miR160 expression module in the roots of the drb4, drb14, and drb24 mutants, we uncovered a previously unknown role for DRB4 in regulating miR160 production. Conclusions: The miR160 expression module forms a central component of the molecular and phenotypic response of Arabidopsis plants to exogenous auxin treatment. Furthermore, DRB1, DRB2, and DRB4 are all required in Arabidopsis roots to control miR160 production, and subsequently, to appropriately regulate ARF10, ARF16, and ARF17 target gene expression.
Keywords: ARF16; ARF17; AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR10 (ARF10); Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis); miR160 expression module; microRNA160 (miR160); root development; synthetic auxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular Manipulation of the miR160/AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR Expression Module Impacts Root Development in Arabidopsis thaliana.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 7;15(8):1042. doi: 10.3390/genes15081042. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202402 Free PMC article.
-
DRB1, DRB2 and DRB4 Are Required for an Appropriate miRNA-Mediated Molecular Response to Osmotic Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 22;25(23):12562. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312562. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684274 Free PMC article.
-
MiR160 and its target genes ARF10, ARF16 and ARF17 modulate hypocotyl elongation in a light, BRZ, or PAC-dependent manner in Arabidopsis: miR160 promotes hypocotyl elongation.Plant Sci. 2021 Feb;303:110686. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110686. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33487334
-
Control of root cap formation by MicroRNA-targeted auxin response factors in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2005 Aug;17(8):2204-16. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.033076. Epub 2005 Jul 8. Plant Cell. 2005. PMID: 16006581 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-directed regulation of Arabidopsis AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR17 is essential for proper development and modulates expression of early auxin response genes.Plant Cell. 2005 May;17(5):1360-75. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.031716. Epub 2005 Apr 13. Plant Cell. 2005. PMID: 15829600 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs and their role in plants: prospective omics-tools for improving growth, development and stress tolerance in field crops.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 20;52(1):249. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10305-9. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39976851 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

