White Tea Aqueous Extract: A Potential Anti-Aging Agent Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Senescence in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 39766976
- PMCID: PMC11728359
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13244034
White Tea Aqueous Extract: A Potential Anti-Aging Agent Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Senescence in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
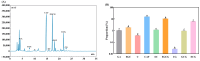
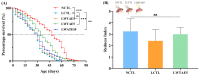
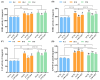
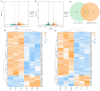
White tea has been scientifically proven to exhibit positive biological effects in combating chronic diseases, including cancer, metabolic syndrome, etc. Nevertheless, the anti-aging activity and mechanism of white tea on organisms exposed to a high-fat diet remain unexplored. Herein, we prepared a white tea aqueous extract (WTAE) from white peony in Fuding and assessed its in vivo antioxidant and anti-aging effects by employing a Drosophila melanogaster senescence model induced by lard, delving into the underlying molecular mechanisms through which the WTAE contributes to lifespan improvement. Notably, the WTAE significantly extended the lifespan of Drosophila fed a high-fat diet and partially restored the climbing ability of Drosophila on a high-fat diet, accompanied by increased activities of copper-zinc superoxide dismutase, manganese-superoxide dismutase, and catalase and decreased lipid hydroperoxide levels in Drosophila. Furthermore, transcriptomic analysis indicated that the WTAE countered aging triggered by a high-fat diet via activating oxidative phosphorylation, neuroactive ligand-receptor interactions, and more pathways, as well as inhibiting circadian rhythm-fly, protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum, and more pathways. Our findings suggest that WTAE exhibits excellent inhibitory activity against high-fat diet-induced senescence and holds promising potential as an anti-aging agent that can be further developed.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; RNA-seq; anti-aging; high-fat diet; white tea aqueous extract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

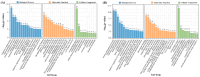

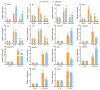
References
-
- Dan A., Chen Y., Tian Y., Wang S. In vivo anti-aging properties on fat diet-induced high fat Drosophila melanogaster of n-butanol extract from Paecilomyces hepiali. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness. 2023;12:1204–1211. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.10.015. - DOI
-
- Wang W., Sun Y. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activities of polyphenol extracted from black garlic. Food Sci. Technol. 2017;37:681–685. doi: 10.1590/1678-457x.30816. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2021N5015/the University-Industry Cooperation Project of the Science and Technology Department in Fujian Provincial of China
- 2021J004/Nanping City Science and Technology Plan Project of China
- 2020L3031/Special Fund for the Central Government to Guide Local Science and Technology Development
- N2020Z009/Co-Funded Project for Technological Innovation in the Resource Chemistry Industry of China
- 2022N0030/Guiding Project of the Science and Technology Department in Fujian Province of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

