The Crosstalk Between Cartilage and Bone in Skeletal Growth
- PMID: 39767569
- PMCID: PMC11727353
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12122662
The Crosstalk Between Cartilage and Bone in Skeletal Growth
Abstract
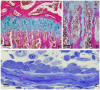
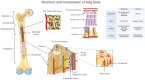
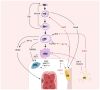
While the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles are formed directly from sheets of undifferentiated mesenchymal cells, most bones in the human body are first formed as cartilage templates. Cartilage is subsequently replaced by bone via a very tightly regulated process termed endochondral ossification, which is led by chondrocytes of the growth plate (GP). This process requires continuous communication between chondrocytes and invading cell populations, including osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and vascular cells. A deeper understanding of these signaling pathways is crucial not only for normal skeletal growth and maturation but also for their potential relevance to pathophysiological processes in bones and joints. Due to limited information on the communication between chondrocytes and other cell types in developing bones, this review examines the current knowledge of how interactions between chondrocytes and bone-forming cells modulate bone growth.
Keywords: cell–cell interactions; chondrocytes; endochondral ossification; growth plate; osteocyte; osteogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Nichols J. UpToDate. 2022. p. 1–50 Normal Growth Patterns in Infants and Prepubertal Children. [(accessed on 25 July 2024)]. Available online: https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/normal-growth-patterns-in-infants-and-p....
-
- Graber E.G. MSD Manual, Professional Version. Merck & Co, Inc.; Rahway, NJ, USA: 2023. Physical Growth of Infants and Children.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

