The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Liver Fibrosis: Friends or Foes?
- PMID: 39767572
- PMCID: PMC11726879
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12122665
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Liver Fibrosis: Friends or Foes?
Abstract
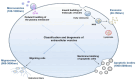
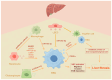
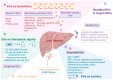
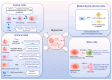
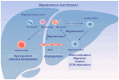
Liver fibrosis represents a common pathway in the progression of various chronic liver diseases towards cirrhosis and liver failure. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-enclosed particles secreted by diverse cell types, including exosomes, microvesicles, apoptotic vesicles, and the recently identified migrasomes. These vesicles can be taken up by recipient cells, thereby modulating their function through the transport of cargo molecules. EVs facilitate intercellular communication and play a significant role in the development of liver fibrosis. Moreover, the detection of EVs in various body fluids offers sensitive diagnostic tools for assessing liver fibrosis. Additionally, EVs may serve as therapeutic targets, potential therapeutic agents, and drug delivery vehicles. This article reviews recent advances in the field of EVs concerning liver fibrosis and related diseases, with a particular focus on the potential role of the newly discovered migrasomes in intracellular crosstalk within the liver.
Keywords: exosomes; extracellular vesicles; intracellular communication; liver fibrosis; migrasomes; therapeutic strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- MacParland S.A., Liu J.C., Ma X.Z., Innes B.T., Bartczak A.M., Gage B.K., Manuel J., Khuu N., Echeverri J., Linares I., et al. Single cell RNA sequencing of human liver reveals distinct intrahepatic macrophage populations. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:4383. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06318-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

