Levo-Stepholidine as a Potential Cognitive Enhancer: Insights into Executive Function and Memory Improvements
- PMID: 39767588
- PMCID: PMC11727210
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12122680
Levo-Stepholidine as a Potential Cognitive Enhancer: Insights into Executive Function and Memory Improvements
Abstract
Background/objectives: Levo-Stepholidine (l-SPD), a compound extracted from Chinese herbs, has the potential to treat psychotic disorders where cognitive deficits are a critical challenge. L-SPD displays a D1R agonism/D2R antagonism pharmacological profile, and its effect on cognitive function is still vague and lacks comprehensive study. Here, we investigated the impact of l-SPD on two core indexes of executive function, working memory and response inhibition, and learning and memory.
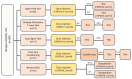
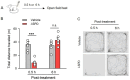
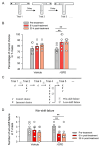
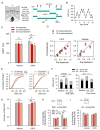
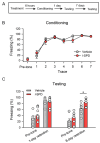
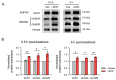
Methods: Using a delayed alternation T-maze task (DAT), we investigated the impact of l-SPD on working memory, evaluated its effect on response inhibition using the stop-signal task (SST), and assessed the impact on learning and memory using trace fear conditioning in Sprague-Dawley rats. We further evaluated its effects on prefrontal glutamate receptor expression using western blot.
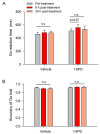
Results: Rats receiving l-SPD made fewer errors in the T-maze, exhibited faster stop action in response to the stop signal, and showed longer-lasting memory retention. Molecular mechanism investigations reveal that l-SPD upregulates the expression of prefrontal glutamate receptors. These results demonstrate that l-SPD improves executive function and memory.
Conclusions: Here, we show the enhancement effect of l-SPD on cognitive function, which provides essential implicants for the treatment of cognitive deficits, which is a critical unmet need in psychiatric care.
Keywords: Chinese herb; D1 receptor agonist; D2 receptor antagonist; Sprague-Dawley rats; antipsychotic agents; cognition; executive function; glutamate receptors; memory; prefrontal cortex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shahrokh N.C., Hales R.E., Phillips K.A., Yudofsky S.C. The Language of Mental Health: A Glossary of Psychiatric Terms. American Psychiatric Publishing; Arlington, VA, USA: 2011.
-
- Sabe M., Pillinger T., Kaiser S., Chen C., Taipale H., Tanskanen A., Tiihonen J., Leucht S., Correll C.U., Solmi M. Half a century of research on antipsychotics and schizophrenia: A scientometric study of hotspots, nodes, bursts, and trends. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022;136:104608. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104608. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

