Cerebrospinal Fluid Classical Biomarker Levels in Mixed vs. Pure A+T+ (A+T1+) Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 39767810
- PMCID: PMC11672946
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12122904
Cerebrospinal Fluid Classical Biomarker Levels in Mixed vs. Pure A+T+ (A+T1+) Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
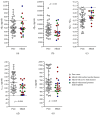
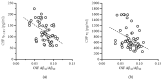
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) may present with pure (typical or atypical) and mixed phenotypes, sometimes causing difficulties in (differential) diagnosis. In order to achieve a diagnostic accuracy as high as possible, the diagnosis of AD during life depends on various biomarkers, including the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers. Methods: Classical CSF AD biomarkers were determined in a total of 61 patients, classified as both beta amyloid- and tau-positive A+T+ (or A+T1+ according to the recently revised Alzheimer Association criteria for diagnosis and staging of AD). Twenty one of these patients fulfilled the criteria for mixed AD (mixed with Lewy bodies, cerebrovascular disease, or normal pressure hydrocephalus), whilst 40 had pure AD. Results: Patients did not differ with respect to gender, education, disease duration, and cognitive status. After controlling for confounding factors, no difference was observed between mixed and pure AD groups in Aβ42 or Aβ42/Aβ40 levels. Although by definition, patients of both groups had abnormal (increased) levels of phospho-tau181, the mixed AD group presented with lower (less abnormal) levels of phospho-tau181 and total tau as compared to the pure group. Conclusions: In patients with AD of comparable cognitive status, mixed AD cases may present with lower levels of tau proteins and, if close to the cut-off values, diagnostic uncertainty may be increased.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; beta amyloid; biomarkers; cerebrospinal fluid; phospho-tau; tau protein.
Conflict of interest statement
G.T., G.P.P., I.T, A.A., C.Z. and A.B. are clinical investigators in the “EVOKE” and “EVOKE plus” trials of semaglutide for early Alzheimer’s disease (NovoNordisk, NCT04777396, and NCT04777409 respectively). G.P.P received fees from Biogen International and from ITF Hellas, as a consultant of advisory boards. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers (Phospho-Tau181, total-Tau, Aβ42, and Aβ40) in Prodromal Stage of Alzheimer's Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;51(4):1069-83. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150731. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 26923009
-
Cerebrospinal fluid Alzheimer biomarkers can be useful for discriminating dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer's disease at the prodromal stage.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018 May;89(5):467-475. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2017-316385. Epub 2018 Jan 10. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29321140
-
CSF Aβ40 and P-Tau181 Might Differentiate Atypical from Typical AD Phenotypes: Preliminary Evidence.Neurodegener Dis. 2022;22(2):83-86. doi: 10.1159/000526888. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Neurodegener Dis. 2022. PMID: 36108600
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus versus Alzheimer's Disease and Subcortical Ischemic Vascular Disease: A Systematic Review.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;68(1):267-279. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180816. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 30741681
-
Clinical indications for analysis of Alzheimer's disease CSF biomarkers.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2013 Oct;169(10):709-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2013.07.024. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2013. PMID: 24016466 Review.
Cited by
-
APOE Genotyping in Cognitive Disorders: Preliminary Observations from the Greek Population.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 1;26(15):7410. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157410. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hyman B.T., Phelps C.H., Beach T.G., Bigio E.H., Cairns N.J., Carrillo M.C., Dickson D.W., Duyckaerts C., Frosch M.P., Masliah E., et al. National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2012;8:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.10.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McKhann G.M., Knopman D.S., Chertkow H., Hyman B.T., Jack C.R., Jr., Kawas C.H., Klunk W.E., Koroshetz W.J., Manly J.J., Mayeux R., et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011;7:263–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

