Deviant Peer Affiliation, Depression, and Adolescent Non-Suicidal Self-Injury: The Moderating Effect of the OXTR Gene rs53576 Polymorphism
- PMID: 39767874
- PMCID: PMC11674054
- DOI: 10.3390/children11121445
Deviant Peer Affiliation, Depression, and Adolescent Non-Suicidal Self-Injury: The Moderating Effect of the OXTR Gene rs53576 Polymorphism
Abstract
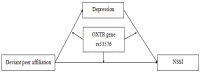
Background: Adolescent non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) has emerged as a progressively widespread and significant public health concern on a global scale. Research has increasingly documented a positive linkage between deviant peer affiliation and adolescent NSSI; however, there is little known about the underlying moderating or mediating mechanism of NSSI. According to the gene × environment interaction perspective, the current study investigated the intermediary function of depression in linking deviant peer affiliation to NSSI among adolescents, while also considering the moderating effect of the OXTR gene rs53576 polymorphism on this intermediary process.
Methods: A total of 469 adolescents (Meanage = 12.81 years; SD = 0.47 years) anonymously finished the study questionnaires. This study used structural equation modeling analysis to verify a moderated mediation model. Gender, age, and family financial difficulties were used as covariates.
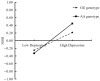
Results: Mediation analyses suggested that the positive connection between deviant peer affiliation and adolescent NSSI was mediated by depression. Moreover, the moderated mediation analyses revealed that deviant peer affiliation increased depression levels, which in turn contributed to increased NSSI among adolescents with the AA genotype. Nevertheless, the correlation failed to reach statistical significance among adolescents possessing the GA and GG genotypes.
Conclusions: These findings emphasize depression's potential as a bridge linking deviant peer affiliation to adolescent NSSI. The AA genotype of the OXTR gene rs53576 emerges as a critical risk factor in the enhancement of this indirect effect. This study provides valuable perspectives for designing intervention strategies aimed at reducing adolescent NSSI.
Keywords: OXTR gene rs53576 polymorphism; adolescent; depression; deviant peer affiliation; non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How and When Deviant Peer Affiliation Influence Non-Suicidal Self-Injury? Testing a Longitudinal Moderated Serial Mediation Model among Chinese Early Adolescents.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2025 Mar 29. doi: 10.1007/s10578-025-01825-3. Online ahead of print. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2025. PMID: 40156667
-
Parental Psychological Control, the Parent-Adolescent Relationship, and Non-suicidal Self-Injury Among Chinese Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of the Oxytocin Receptor Gene rs53576 Polymorphism.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2023 Dec 18. doi: 10.1007/s10578-023-01646-2. Online ahead of print. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2023. PMID: 38110758
-
Deviant Peer Affiliation and Non-Suicidal Self-Injury among Chinese Adolescents: Depression as a Mediator and Sensation Seeking as a Moderator.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 6;18(16):8355. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18168355. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34444105 Free PMC article.
-
Peer victimization, depression, and non-suicidal self-injury among Chinese adolescents: the moderating role of the 5-HTR2A gene rs6313 polymorphism.Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2022 Dec 27;16(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s13034-022-00532-4. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2022. PMID: 36575481 Free PMC article.
-
Parent-Adolescent Conflict, Peer Victimization, and Internet Gaming Disorder Among Chinese Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of OXTR Gene rs53576 Polymorphism.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024 Dec;55(6):1634-1643. doi: 10.1007/s10578-023-01523-y. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024. PMID: 36930441
Cited by
-
Longitudinal associations between relative deprivation and non-suicidal self-injury in early adolescents: a moderated mediation model.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Mar 21;16:1553740. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1553740. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40191108 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of menstrual characteristics with non-suicidal self-injury: results from six universities in China.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):2217. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23260-8. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40604710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu R., Huang J., Ying J., Gao Q., Guo J., You J. Behavioral inhibition/approach systems and adolescent nonsuicidal self-injury: The chain mediating effects of difficulty in emotion regulation and depression. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2021;175:110718. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2021.110718. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources