The Importance of Hearing Screening and Central Auditory Processing in School-Aged Children
- PMID: 39767879
- PMCID: PMC11674852
- DOI: 10.3390/children11121450
The Importance of Hearing Screening and Central Auditory Processing in School-Aged Children
Abstract
Background/objectives: The aim of the study was to evaluate the prevalence of undiagnosed hearing impairment or central auditory processing disorders in children from I and VIII grades of primary schools in Warsaw.
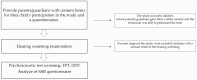
Methods: The participants in the study were 15,659 pupils from classes I and VIII attending primary schools in Warsaw. As part of the study, the hearing threshold for air conduction at frequencies of 0.5-8 kHz was determined, and a test assessing central auditory processing was performed: FPT (Frequency Pattern Test), DDT (Dichotic Digit Test), the Auditory Behaviour Scale (SAB), and an interview questionnaire developed for the program.
Results: Abnormal test results were found in 1946 children, of which abnormal hearing screening test results were found in 678 children tested, while reduced central auditory processing results were found in 1268 children.
Conclusions: The program implemented draws attention to the fact that tests of central auditory processing are included in the testing protocol. As has been shown, peripheral hearing testing alone is not sufficient to exclude abnormalities concerning the sense of hearing.
Keywords: central auditory processing disorder; hearing screening; pure tone audiometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
Dichotic Digits Test Performance Across the Ages: Results From Two Large Epidemiologic Cohort Studies.Ear Hear. 2017 May/Jun;38(3):314-320. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000386. Ear Hear. 2017. PMID: 27941404 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the degree of hearing loss using click auditory brainstem response in babies referred from newborn hearing screening.Ear Hear. 2013 May-Jun;34(3):361-9. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0b013e3182728b88. Ear Hear. 2013. PMID: 23340456
-
Diagnostic Hearing Assessment in Schools: Validity and Time Efficiency of Automated Audiometry.J Am Acad Audiol. 2016 Jan;27(1):42-8. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.15041. J Am Acad Audiol. 2016. PMID: 26809325
-
[Otoacoustic emissions, auditory evoked potentials, pure tone thresholds and speech intelligibility in cases of auditory neuropathy].HNO. 2000 Jan;48(1):28-32. doi: 10.1007/s001060050005. HNO. 2000. PMID: 10663046 Review. German.
-
Audiometry and other hearing tests.Handb Clin Neurol. 2016;137:157-76. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63437-5.00011-X. Handb Clin Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27638069 Review.
References
-
- Dobie R.A., Van Hemel S., National Research Council . Hearing Loss: Determining Eligibility for Social Security Benefits. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC, USA: 2004. Basics of sound, the ear, and hearing. - PubMed
-
- Matusiak M., Oziębło D., Ołdak M., Obrycka A., Kaczmarek L., Skarżyński H. Ocena wyników leczenia głuchoty prelingwalnej za pomocą wszczepienia implantu ślimakowego w świetle funkcjonalnego polimorfizmu genów MMP9 i BDNF. Nowa Audiofonol. 2022;10:11–18. doi: 10.17431/10.2.1. - DOI
-
- Katz J. Handbook of Clinical Audilogy. 7th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2014.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous